Examples can be found here. Installation can be found here.
Cpp-lazy is a fast and easy lazy evaluation library for C++11/14/17/20. This is a fast library because the library does not allocate any memory. Moreover, the iterators are random-access where possible. Therefore operations, for example std::distance, are an O(1) operation, either by "overloading" the std::distance/std::next functions using ADL lookup, or by adding a std::random_access_iterator_tag. Furthermore, the view object has many std::execution::* overloads. This library uses one (optional) dependency: the library {fmt}, more of which can be found out in the installation section.
Example:
#include <Lz/Map.hpp>
int main() {
std::array<int, 4> arr = {1, 2, 3, 4};
std::string result = lz::map(arr, [](int i) { return i + 1; }).toString(" "); // == "2 3 4 5"
}- C++11/14/17/20; C++20 concept support; C++17
executionsupport (std::execution::par/std::execution::seqetc...) - Easy print using
std::cout << [lz::IteratorView]orfmt::print("{}", [lz::IteratorView]) - Compatible with old(er) compiler versions; at least
gccversions =>4.8&clang=>5.0.0(previous versions have not been checked, so I'd say at least a compiler with C++11 support). - Tested with
-Wpedantic -Wextra -Wall -Wno-unused-functionand/W4for MSVC - One optional dependency (
{fmt}) std::formatcompatible- STL compatible
- Little overhead
- Any compiler with at least C++11 support is suitable
- Easy installation
- Clear Examples
- Readable, using method chaining
Lazy evaluation is an evaluation strategy which holds the evaluation of an expression until its value is needed. In this
library, all the iterators are lazy evaluated. Suppose you want to have a sequence of n random numbers. You could
write a for loop:
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
std::uniform_int_distribution dist(0, 32);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
std::cout << dist(gen); // prints a random number n times, between [0, 32]
}This is actually exactly the same as:
// If standalone:
std::cout << lz::random(0, 32, n);
// If with fmt:
fmt::print("{}", lz::random(0, 32, n));Both methods do not allocate any memory but the second example is a much more convenient way of writing the same thing. Now what if you wanted to do eager evaluation? Well then you could do this:
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
std::uniform_int_distribution dist(0, 32);
std::vector<int> randomNumbers;
std::generate(randomNumbers.begin(), randomNumbers.end(), [&dist, &gen]{ return dist(gen); });That is pretty verbose. Instead, try this for change:
std::vector<int> randomNumbers = lz::random(0, 32, n).toVector();I want to search if the sequence of random numbers contain 6.
In 'regular' C++ code that would be:
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
std::uniform_int_distribution dist(0, 32);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (gen(dist)) == 6) {
// do something
}
}In C++ using this library and because all iterators in this library are STL compatible, we could simply use std::find:
auto random = lz::random(0, 32, n);
if (std::find(random.begin(), random.end(), 6) != random.end()) {
// do something
}
// or
if (lz::contains(random, 6)) {
// do something
}So by using this lazy method, we 'pretend' it's a container, while it actually is not. Therefore it does not allocate any memory and has very little overhead.
I understand where you're coming from. You may think it's more readable. But the chances of getting bugs are
bigger because you will have to write the whole loop yourself. On average
about 15 – 50 errors per 1000 lines of delivered code contain
bugs. While this library does all the looping for you and is thoroughly tested using catch2. The lz::random for-loop
equivalent is quite trivial to write yourself, but you may want to look at lz::concat.
To guarantee the best performance, some iterators have custom next/distance implementations. If you use these functions, please be sure to do it as follows:
auto view = lz::chunks(array, 3);
// Calculate distance:
auto dist = view.distance(); // or view.size()
// Get nth element:
auto nth = view.next(2);Or you can do:
auto view = lz::chunks(array, 3);
// Calculate distance:
using std::distance; using lz::distance;
auto dist = distance(view.begin(), view.end());
// Get nth element:
using std::next; using lz::next;
auto nth = next(view.begin(), 4);If, for some reason, you do not wish to do this, then be sure to use lz::next/lz::distance for the following iterators:
CartesianProductIteratorcreated bylz::cartesian::beginRangecreated bylz::range::beginTakeEveryIteratorcreated bylz::takeEvery::beginChunksIteratorcreated bylz::chunks::beginFlattenIteratorcreated bylz::flatten::beginExcludeIteratorcreated bylz::exclude::begin
- Clone the repository
- Specify the include directory to
cpp-lazy/include. - Include files as follows:
// Important, preprocessor macro 'LZ_STANDALONE' has to be defined already
#include <Lz/Map.hpp>
int main() {
std::array<int, 4> arr = {1, 2, 3, 4};
std::string result = lz::map(arr, [](int i) { return i + 1; }).toString(" "); // == "1 2 3 4"
}- Clone the repository
- Specify the include directory to
cpp-lazy/includeandfmt/include. - Define
FMT_HEADER_ONLYbefore including anylzfiles. - Include files as follows:
#define FMT_HEADER_ONLY
#include <Lz/Map.hpp>
int main() {
std::array<int, 4> arr = {1, 2, 3, 4};
std::string result = lz::map(arr, [](int i) { return i + 1; }).toString(" "); // == "2 3 4 5"
}If you want to use the standalone version, then use the CMake option -D CPP-LAZY_USE_STANDALONE=ON or set(CPP-LAZY_USE_STANDALONE TRUE). This also prevents the cloning of the library {fmt}.
Add to your CMakeLists.txt the following:
include(FetchContent)
FetchContent_Declare(cpp-lazy
GIT_REPOSITORY https://github.com/MarcDirven/cpp-lazy
GIT_TAG ... # Commit hash
UPDATE_DISCONNECTED YES)
FetchContent_MakeAvailable(cpp-lazy)
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} cpp-lazy::cpp-lazy)Clone the repository using git clone https://github.com/MarcDirven/cpp-lazy/ and add to CMakeLists.txt the following:
add_subdirectory(cpp-lazy)
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} cpp-lazy::cpp-lazy)Or add cpp-lazy/include to the additional include directories in e.g. Visual Studio.
#include <Lz.hpp> // or e.g. #include <Lz/Filter.hpp>
int main() {
// use e.g. lz::filter
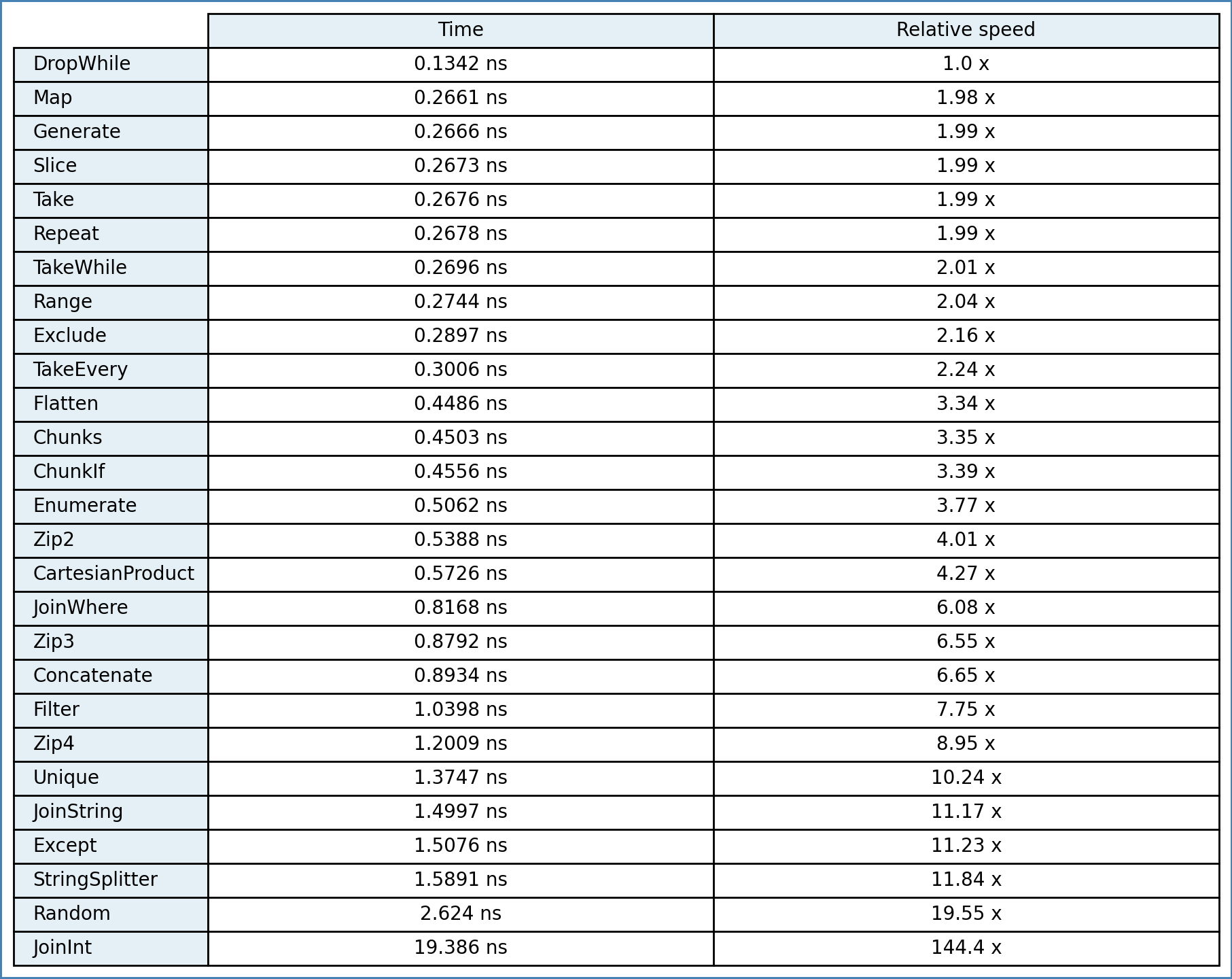
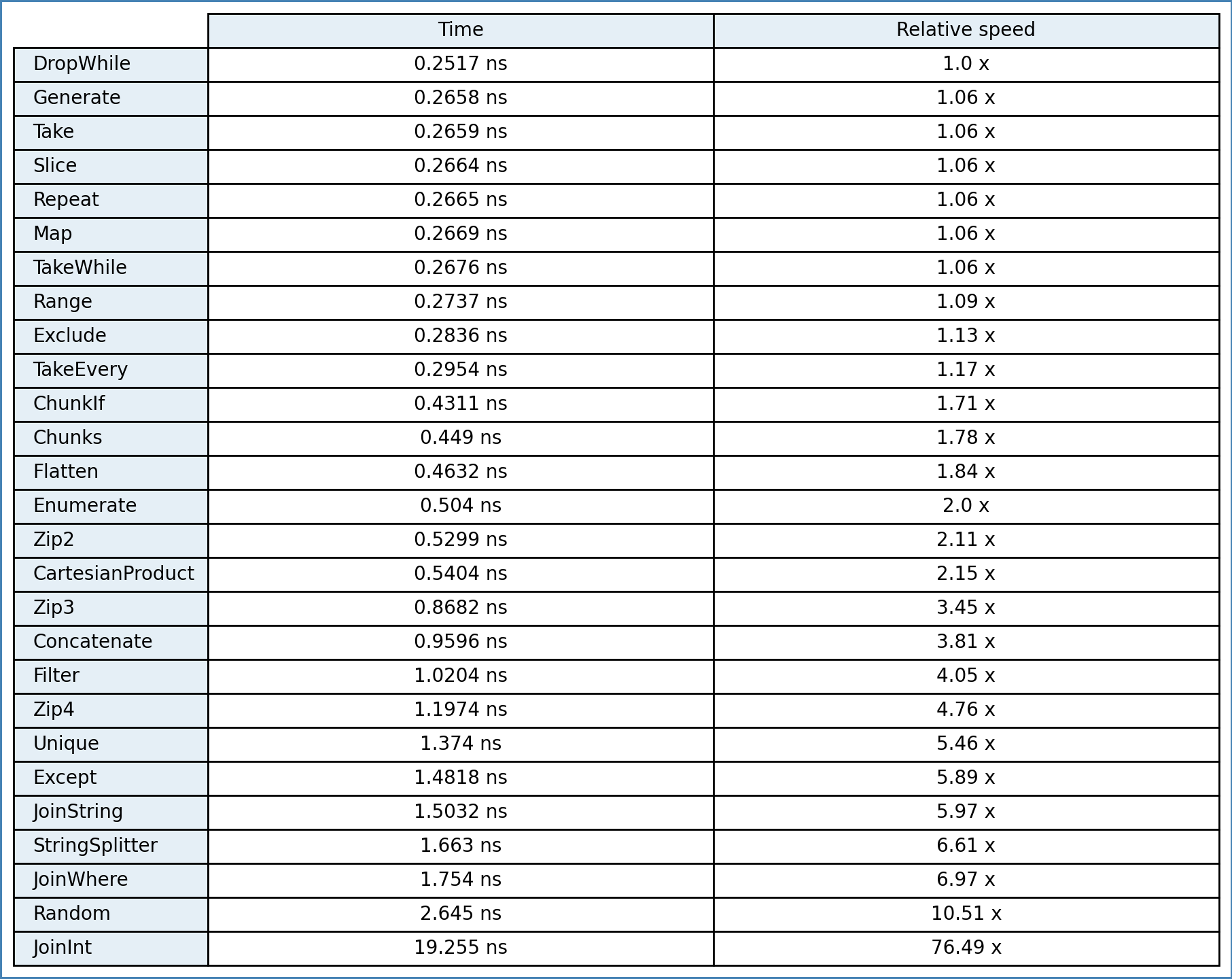
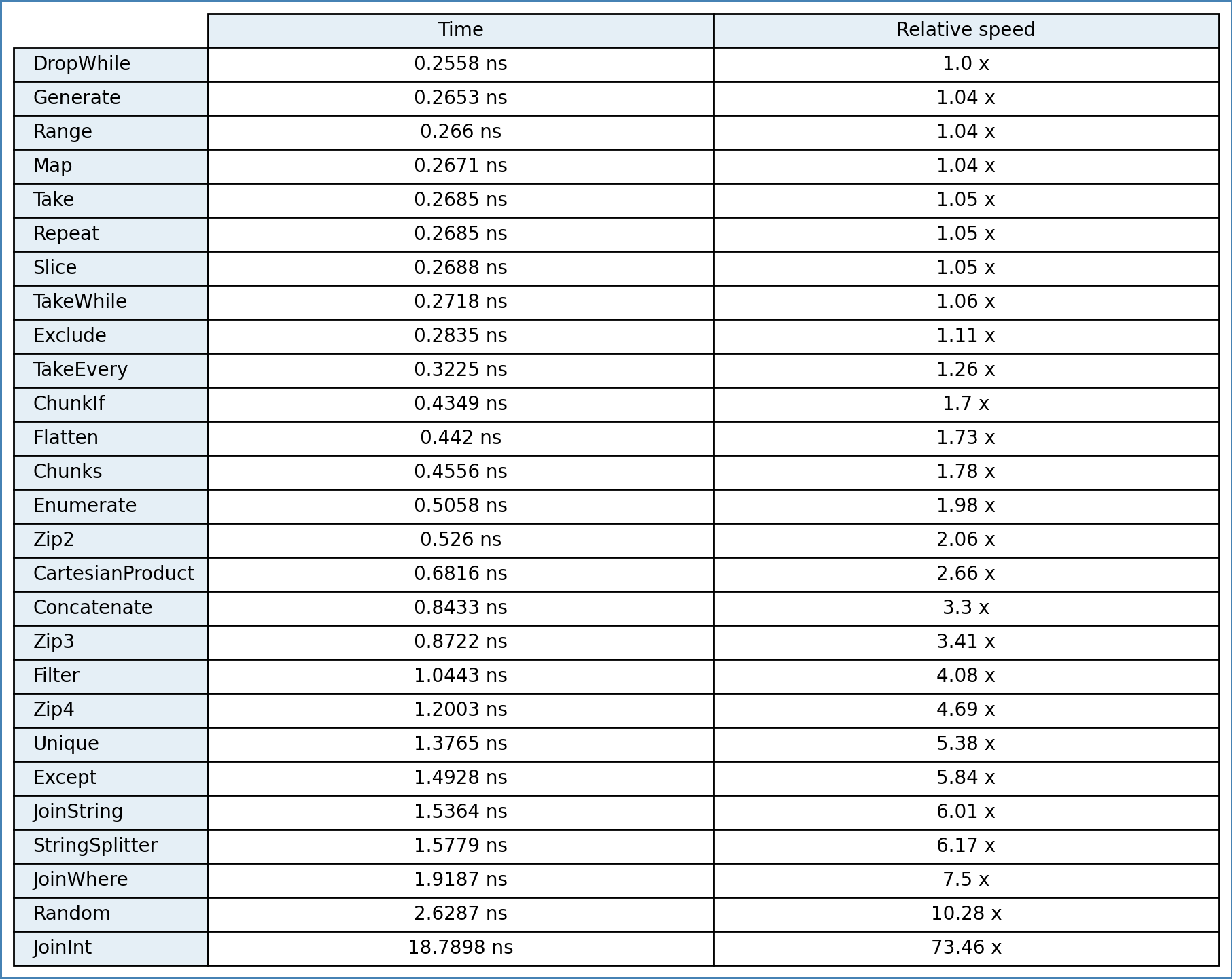
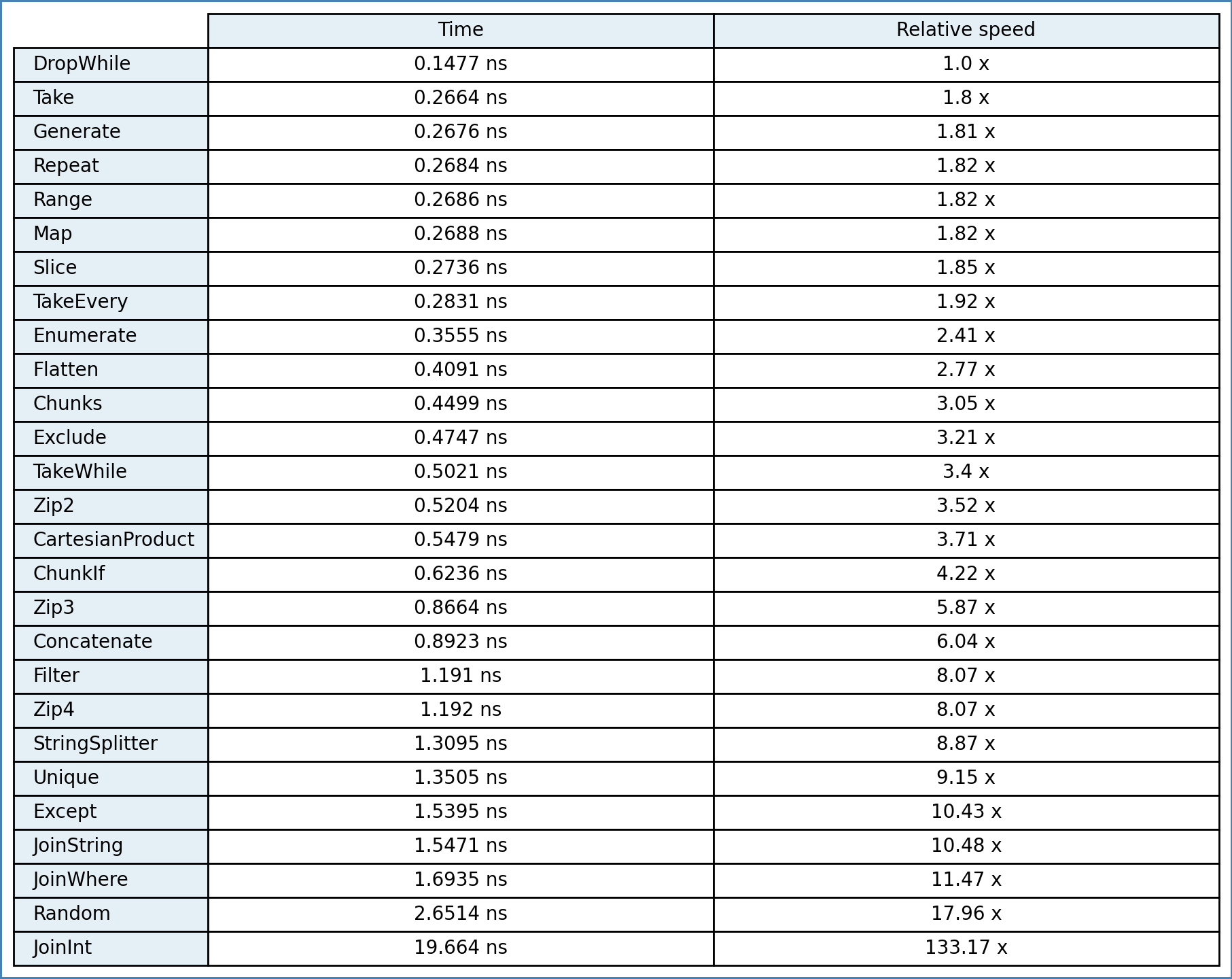
}The time is equal to one iteration. Compiled with: winlibs-x86_64-posix-seh-gcc-10.2.1-snapshot20200912-mingw-w64-7.0.0-r1
C++11
C++14
C++17
C++20
Special thanks to the JetBrains open source programme.