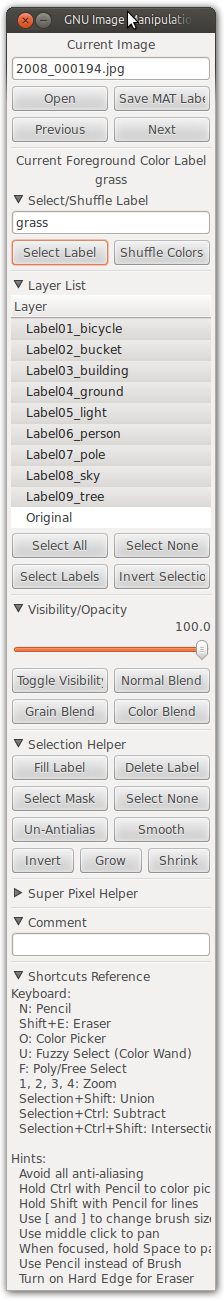
Image labeling is a common task in computer vision where humans are used to generate a ground truth data set to act both as training data for computer vision algorithms and testing benchmarks for methods that perform semantic segmentation algorithms. The label here is an assignment of a value (or possibly multiple values) to each pixel in the image. These values are usually integers which map to semantic categories such as "train" and "person". Since labels are assigned to each pixel the task is inherently a painting task. It then makes sense to use a painting program to perform hand labeling. This toolbox seeks to facilitate this by working with the GNU Image Manipulation Program (GIMP) thus providing access to the following features and more:
- Canvas zoom and pan
- Pencil tool with multiple brushes and variable brush sizes
- Free form and polygonal select tool
- Color wand select tool
- Color select tool
- Selection morphology operators
- Selection color fill
- Foreground extraction tool
- Multiple blend modes and blend control
The toolbox is written as a Python plugin for GIMP. Its interface is built using PyGTK which is a Python wrapper for the Gnome Toolkit (GTK). It currently exists as a single Python script.
- NumPy for array manipulation (required)
- SciPy for MATLAB
.matfile I/O (required) - Scikit-Image for SLIC segmentation algorithm (optional)
The plugin was developed and tested on Ubuntu 13.10 and 12.04 with GIMP 2.8. Installation of NumPy and SciPy can be taken care of easy on Ubuntu using the following:
sudo apt-get install python-pip python-setuptools python-numpy python-scipy
sudo pip install numpy scipy
For Mac OS X and Windows consider using the binary package installers provided by the maintainers.
Also uses appdirs, specifically the file https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ActiveState/appdirs/2727a1b0444405a8728052512f02f26884528d64/appdirs.py included directly. Thus I need to honor the MIT License appropriately.
Assuming GIMP 2.8 is installed, installation of the toolbox on Ubuntu is just a matter of creating a symlink to or copying both label-toolbox.py and appdirs.py to $HOME/.gimp-2.8/plug-ins. On Linux and Mac OS X remember to give label-toolbox.py executable permissions (e.g. chmod ugo+x label-toolbox.py).
The following instructions are "from memory" and should work but have not been tested on a fresh machine.
- Python 2.7 should already be available.
- Install
pipandgcc.sudo apt-get install -y python-pip python-dev python-setuptoolssudo apt-get install -y gcc g++ gfortran make
- Install NumPy and SciPy.
sudo apt-get install -y cython python-numpy python-scipysudo pip install --upgrade cythonsudo pip install --upgrade numpysudo pip install --upgrade scipy
- [OPTIONAL] Install SciKit-Image.
sudo pip install scikit-image
- Install GIMP 2.8.
- http://www.gimp.org/downloads/
- If you're on Ubuntu 12.04 you can get an updated PPA here.
- Run GIMP 2.8 so that it can initialize itself and the appropriate plug-in folder.
- Install plug-in.
cd $HOME/.gimp-2.8/plug-ins/git clone https://github.com/vietjtnguyen/gimp-image-labeling-toolbox.gitln -s gimp-image-labeling-toolbox/appdirs.py .ln -s gimp-image-labeling-toolbox/label-toolbox.py .
- Close GIMP and reopen it.
- Create a new, blank image.
- Open the toolbox via the file menu
Toolbox > Labeling.
The following instructions worked in my testing for Windows 7 64-bit and Windows 8 64-bit.
- Install Python 2.7 32-bit.
- https://www.python.org/download/releases/2.7.6
- It is important that you install the 32-bit version (e.g. https://www.python.org/ftp/python/2.7.6/python-2.7.6.msi) because the Python that GIMP installs on its own is 32-bit.
- Install NumPy for Python 2.7 32-bit.
- Install SciPy for Python 2.7 32-bit.
- [OPTIONAL] Install SciKit-Image for Python 2.7 32-bit.
- Install GIMP 2.8.
- Run GIMP 2.8 so that it can initialize itself and the appropriate plug-in folder.
- Download the following source files to
C:\Users\<your user name>\.gimp-2.8\plug-ins\. - Close GIMP and reopen it.
- Create a new, blank image.
- Open the toolbox via the file menu
Toolbox > Labeling.
What's going on here is GIMP 2.8 installs its own Python binary. As a result any dependencies (e.g. NumPy, SciPy) you install on your machine are available to the Python 2.7 you install (C:\Python27 by default) but not immediately available to GIMP and the Python plug-ins it runs. What we do here is install Python 2.7 as an install target for our dependencies. The toolbox will then update its sys.path to look for the dependencies in the normally installed Python 2.7 (see commit c910e15dbb). Since we match the Python binary that GIMP installs (v2.7, 32-bit) the dependencies will also work for the GIMP Python install.
Installation on Mac OS X still requires further testing. GIMP appears to also install its own Python binary on Mac OS X.
When the toolbox opens an image, say at /path/to/my-image.jpg, it does four things (see openImageButtonClicked):
- Loads the label name to label integer mapping file (see
loadMetaData). It looks for this file at/path/to/../map.txt. - Loads the original image (see
loadImage). This is the image that is opened so the toolbox already knows where it is. - Loads the label
.matfile (seeloadLabelMat). The toolbox looks for this at/path/to/../label/my-image.mat. - Loads the comment associated with the image (see
loadComment). The toolbox finds this file at/path/to/../comment/my-image.txt.
The /label folder contains the .mat array files that store the labels themselves. The /comment folder contains text files (simple UTF-8 text files) that have the per-image comments. A text file per-image is optional; the folder could be empty to begin with.
/path/to/map.txt
/path/to/image/2010_002080.jpg
/path/to/comment/2010_002080.txt
/path/to/label/2010_002080.mat
- Open GIMP
- Create a new blank image
- Open
Toolbox > Labelingin the menu - Open image using toolbox's
Open Imagebutton - Edit label image on label layer, avoiding anti-aliasing everywhere
- Save label using toolbox's
Save MAT Labelbutton - Repeat step 4 for more images, optionally using the
PreviousandNextbuttons.
The open/save state of an image when using the toolbox exists independently of GIMP's open/save states. When using the toolbox use only the Open Image and Save MAT Label buttons on the toolbox.
When the toolbox loads an image it will load the original image into a layer named Original and load all of the label layers on top of the Original layer. The color map is randomized on load and can be shuffled further using the Shuffle Colors button. The only changes that are saved are edits to layers whose name starts with Label (e.g. LabelGrass, Label_wabalabaDUBDUB. Changes to any other layer are discarded/ignored.
Remember that tools will only operate on the currently selected layer. The list of layers should be in the interface by default. If not you can bring it up using Ctrl+L.
I personally suggest using GIMP in single-window mode. This can be activated at Windows > Single-Window Mode.
Users must pay attention to whether or not their selection is anti-aliased. Anti-aliased selections will result in corrupted labels since blended label colors have no semantic meaning and will most likely fall outside the label color map. Be wary of the anti-aliased options on your selection tool or use the Un-Antialias button in the toolbox under Selection Helper.
The toolbox window will automatically float on top of the GIMP window but will still capture focus. It is an entirely separate application from GIMP. This means if the toolbox has window focus then GIMP keyboard shortcuts will not work. To use keyboard shortcuts you must bring the GIMP window back in focus by clicking on it or Alt-Tabbing to it.
- The toolbox is currently very tall. Fully expanded it is nearly 1000 pixels tall. Sections can be collapsed to help it fit on smaller screens.
- I would have put buttons on the toolbox for the common tools but the GIMP plugin API does not provide functionality for selecting tools.
- The comment text field is saved on the fly. Each edit updates the text file immediately.
- Write a full tutorial
- Document
.matlabel array format - Document Super Pixel Helper
- Reduce toolbox height, maybe use two columns?
- Support alternative label formats (e.g.
.ipy, packed binary integers, etc.) - Add configuration file for supporting options such as default blend mode, etc.