This repository houses survey data and Python scripts related to a case study performed as part of UMass Dartmouth's CIS362 Empirical Methods course. The purpose of the case study was to gauge the impact that social media use at an early age has on the formation of an individual's social skills. This README contains selections of information from the research paper written as part of this project. The full paper can be accessed under docs/Intergenerational Social Skills and Social Media Usage (Report).pdf.
The purpose of this case study was to determine if social media usage at an early age has an influence on the formation of certain social skills. We created three sets of social skills questions and sent them to a focus group of 32 participants over the course of 2 weeks, with 8 individuals representative of the following generational brackets: Baby Boomer (53+ yrs. old), Gen X (36-52 yrs. old), Millennial (23-35 yrs. old), and Gen Z (18-22 yrs. old). Questions were developed to determine an individual's likelihood to exhibit a particular social skill. 6 social skills were studied: "directness", "empathy", "meaningful discussion", "precise communication", "idiom comprehension", and "cultural literacy". Each social skill was placed into one of 2 categories. These categories were “Physical Social Skills”; social skills most applicable to in-person interaction (directness, empathy, meaningful discussion), and “Internet Social Skills”; skills most applicable to online communications (precise communication, idiom comprehension, cultural literacy).
Findings suggest that Baby Boomers are more confrontational and direct than all other generations studied, and are severely inept in Internet Social Skills. Our data also suggests that Gen X are adept in empathy, but also severely lacking in Internet Social Skills. Both Millennials and Gen Z are increasingly adept in expressing Internet Social Skills, with empathy remaining the highest Physical Social Skill between both generations. Thus, the data would indicate that early exposure to social media makes an individual more adept in expressing Internet Social Skills while producing no notable difference for any Physical Social Skills.
...
...
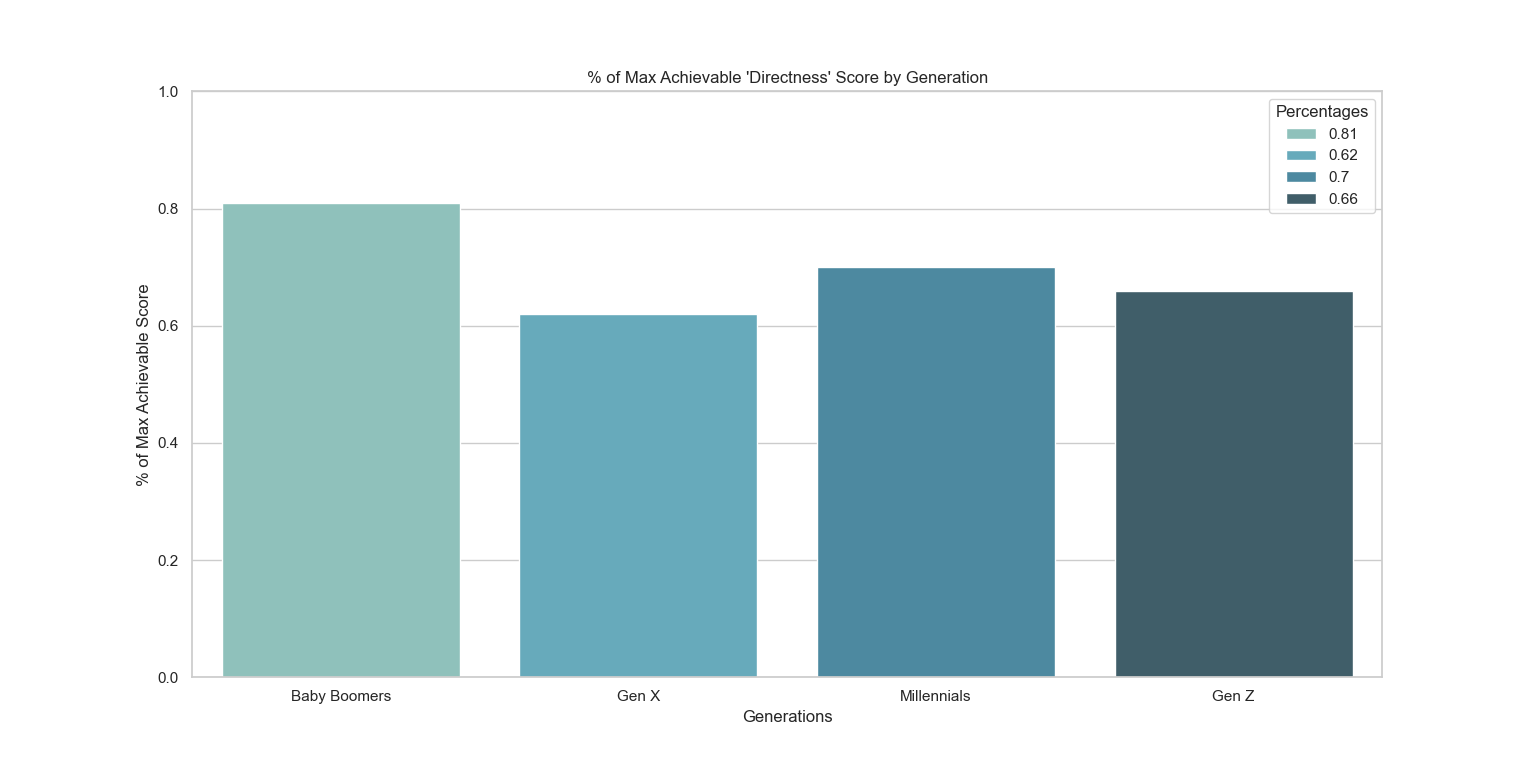
Fig. 1 - “Directness” Score Per Generation
The first Physical Social Skill we wanted to analyze was an individual’s “Directness”, or ability to be confrontational in their actions (not necessarily in an aggressive manner). In these questions, the individuals were presented with a problem and each answer was an action the individual could take that varied in its degree of “Directness”. The graph shown above represents the percent of how many points out of the maximum amount of achievable points each generation scored (out of 72). Boomers received the largest score of 81%. This shows that Baby Boomers have the highest tendency to be direct with their face-to-face interactions with other individuals. Millennials and Gen Z scores are approximately the same, standing at 62% and 68% respectively. This suggests that either generation has a lesser tendency to be direct in their actions in comparison to Baby Boomers. Gen X received a score of only 62%. This is the lowest score for “Directness”, and suggests that Gen X is the most likely of the four generations to avoid direct interactions if given the opportunity.
...
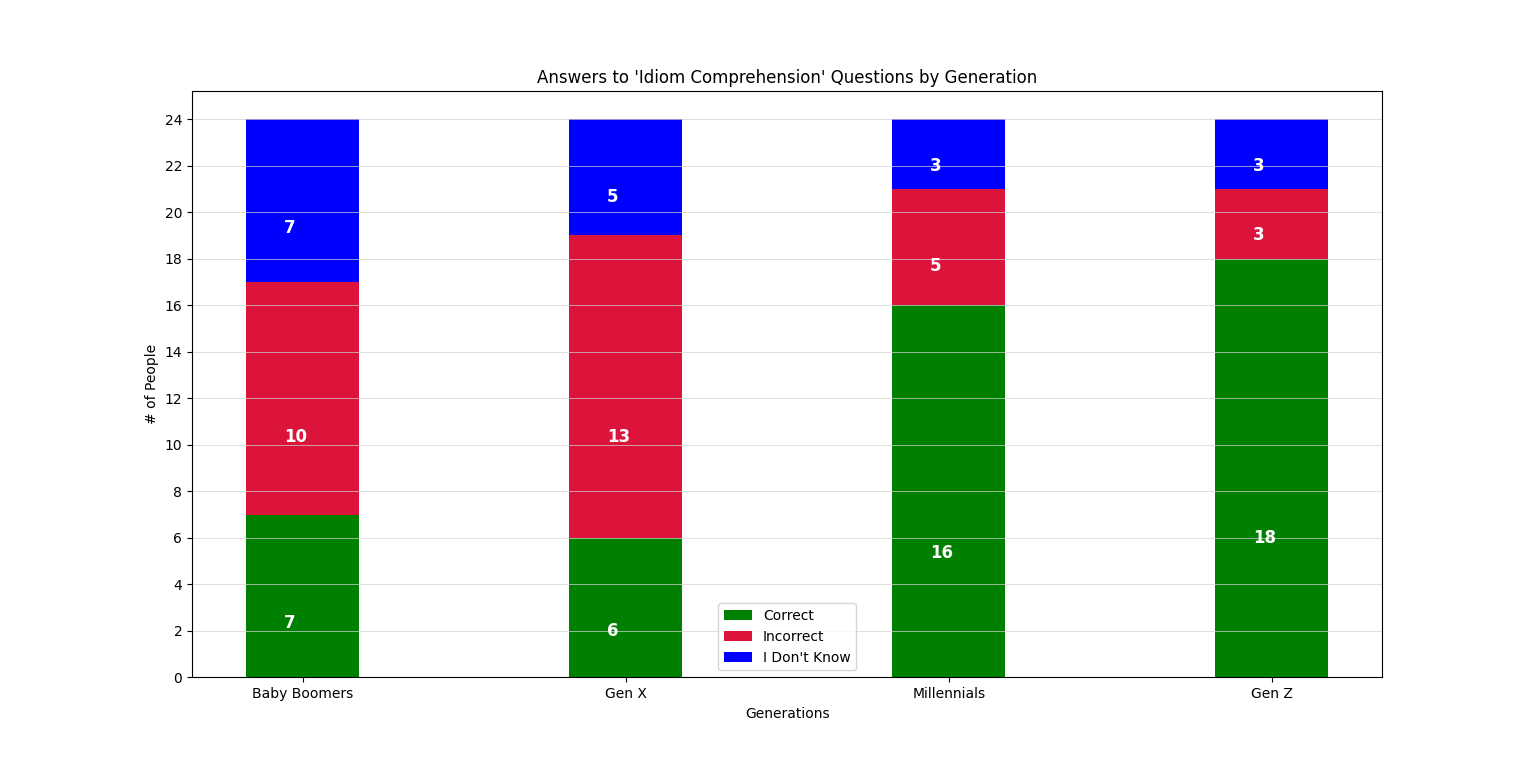
Fig. 5 - “Idiom Comprehension” Responses Per Generation
For our second Internet Social Skill, we wanted to determine an individual's ability to comprehend concepts through novel expressions (“novel expression” being synonymous with “slang”). When creating these questions, we chose a set of contemporary expressions we determined to be well-known by avid users of the internet. Gen Z received the most correct answers of 18 followed by Millennials who received 16 correct answers. This data fell in-line with our initial predictions, as we expected younger generations to be able to correctly identify the meanings of our selected idioms (“yeet”, “no cap”, “salty”, etc.). Baby Boomers and Gen X have 7 and 6 correct answers respectively. What surprised us the most about this dataset was the number of incorrect answers received from both Gen X and the Baby Boomers. Given an expression where the meaning can’t be derived from the expression itself and exists solely within a cultural context, an individual should either be able to correctly identify it's meaning or claim that they do not know. Instead, we received many incorrect answers. This willingness to guess the meaning instead of claiming ignorance may be indicative of a sense of curiosity, and willingness to learn and engage with the use of such expressions.
...
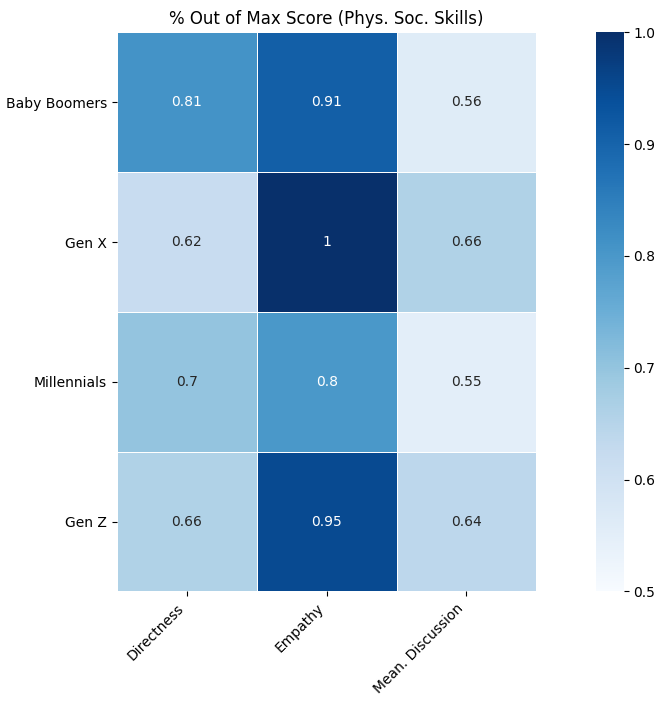
Fig. 7 - % of Max Score Achieved per Generation (Physical Social Skills)
The above heatmap represents the percent of points scored out of the maximum achievable amount of points for each Physical Social Skill. The data was derived from the quotient of dividing the number of points a particular generation scored in a category by the maximum number of points a generation could have earned (72). Since no generation scored below 50% in any category, the graph was scaled to fit a range of .5-1, making it easier to observe any minute differences in data between each category. For the scores of Physical Social Skills, Baby Boomers received two of the higher scores and one of the lowest scores when compared to the other generations. Boomers scored 81% and 91% in Directness and Empathy respectively. This shows that Baby Boomers are more confrontational and empathetic towards their peers. Boomers scored a 56% in Meaningful Discussion, thus indicating that like Millennials (who received only 55%) are amongst the least likely of the 4 generations to feel engaged during a conversation with their peers. Gen X received the lowest score of 62% in Directness and the highest scores in Empathy and Meaningful Discussion of 100% and 66% respectively. The data would suggest that people belonging to Gen X are less likely to directly engage someone, but are more likely to feel empathy and hold meaningful discussions with the people they are not personally familiar with. Millennials received the lowest scores in Empathy and Meaningful Discussion when compared to the other generations. When compared to the other generations, Millennials received the second-largest score in Directness of 70%. This would suggest that Millennials are confrontational people, albeit less than Baby Boomers. Since they hold an 80% for Empathy and 55% for Meaningful Discussion, this would suggest that Millennials are less likely to feel empathetic towards their peers as well as feel engaged when they are conversing. Gen Z received one of the lower scores in Directness by only receiving 66%. Gen Z also received one of the higher scores in Empathy and Meaningful Discussion of 95% and 64% respectively. This data would suggest that Gen Z are more likely to feel engaged and open when situations arise as well as feel more empathetic towards their peers. The data also indicates that Gen Z is less likely to directly converse with their peers. There seems to be no observable pattern in terms of a given Physical Social Skill continually increasing or decreasing as an individual’s exposure to social media happens at a younger age. Thus, it may be possible that there are other factors that contribute to the development of such in-person social skills.
...
...
Since neither Baby Boomers or Gen X were exposed to social media at a young age, Millennials and Gen Z show a significant uptick in the expression of Internet Social Skills, earning the highest and second-highest scores in every category. In contrast to the Physical Social Skill Data, this data clearly indicated a trend taking place, where the younger an individual became, the higher their scores became in every Internet Social Skills category. Thus we can confidently say that an individual will exhibit stronger Internet Social Skills as they are exposed to social media at a younger age. Other research indicates that individuals who lack self-presentational skill (Physical Social Skills) are more likely to prefer online social interaction over face-to-face communication[3]. Given this information, we can hypothesize that as individuals become exposed to social media at a younger and younger age, they will experience a continued degradation of in-person social skills. Exactly which social skills will be affected remains unclear at this time.
Daniel Mello - https://github.com/shouldworkright
Eliel Mares
Stephen Yezukevicz