The scapy code within this repo has been cloned from: https://github.com/nimai/mptcp-scapy. I DO NOT OWN ANY OF THE SCAPY CODE WITHIN THIS REPOSITORY. The original material from this repository only include the python modules in the root folder, used to setup the network scenarios and execute the attacks. These scripts have been developed as employee at Intel in collaboration with KTH University and the Polytechnic of Turin, all rights reserved. Intel and I do not take responsibility of any misuse of this tool for illegal activities.
********** Documentation**********
- Reference document: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7430
The ADD_ADDR attack is addressed in section 2 of the RFC 7430 document. The document provides a high-level overview of the vulnerability affecting the current version of the MPTCP protocol and how it can be exploited to hijack an MPTCP connection. It is important to underline that the vulnerability affects the protocol itself, and it can be found in any implementation. For our experiment we will use two machines running the Linux kernel implementation from: http://multipath-tcp.org/
Simply clone this repository locally on your Linux machine (I tested this code on Ubuntu 14.04 LTS). Your Linux machine will NOT need to run a MPTCP compatible kernel to hijack the connection, since all the packets are sniffed/generated in user space by the Scapy code contained in the repository itself.
Next, you will need two User Mode Linux virtual machines running a MPTCP compatible kernel and communicating using netcat (more on that later). These two VMs can be automatically installed and configured using the setup.py module from the official page:
Please, follow the instruction reported on this web page in order to obtain and run the two UML virtual machines. Refer to the section Network scenario to visualize the environment being setup by the automated scripts.
This is the scenario we are going to setup:
At the moment, the Scapy attacking tool has been designed to hijack a specific kind of communication, involving messages exchange via netcat. This is the step-by-step guide to attack the netcat communication:
- Open two terminal windows and run the client.sh and server.sh scripts to launch the UML virtual machines (user/password: root)
On the server machine, run the following (you can use a TCP Port of your choice here):
netcat -l -p 33443
On the client machine, we first need to disable one of the two network interfaces, namely eth1. This is necessary due to some limitations currently affecting the Scapy tool and the attacking script (the connection will still be MPTCP, with a single subflow):
ifdown eth1
Now you can run netcat on the client, too:
netcat 10.2.1.2 33443
- Try to exchange messages between client and server to verify that communication is active.
- Now we can start the attack opening a new terminal on our local machine (it is necessary to start the Scapy script AFTER having established the netcat connection).
Go to the folder were you downloaded the Scapy tool and type the following:
sudo python test_add_address.py 10.1.1.1 10.2.1.2 10.1.1.2 tap2 tap0
NOTE: If an import error appears, try to install the missing dependencies with:
sudo apt-get install python-netaddr
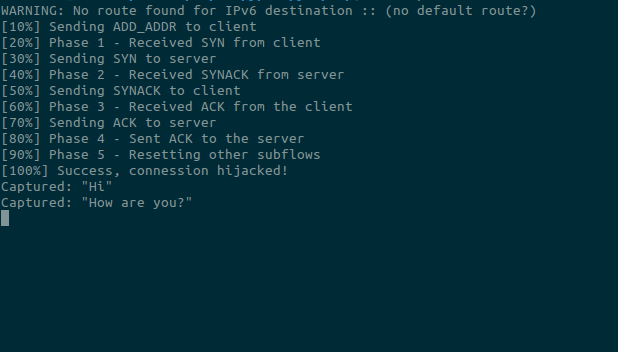
- Go back to the client UML terminal and start sending messages to the server. You should notice that while the messages exchange goes on, the attacking script progresses. IMPORTANT: it might be that the script gets stuck (it shouldn't take more than a few seconds to complete). If that is the case, close netcat and start again from step 2.
- If you reach 100% in the attack process, just try to send a message from the server to the client and you will notice that the messages are now sent to the attacking machine instead. Further improvements would allow to also answer back to the server, thus impersonating the client.
In the document RFC 7430, the attack is presented as "off-path active". As expressed by the document, to perform an off-path attack, the attacker needs to know the following pieces of information:
- the four-tuple: IP and port for both source and destination;
- valid ACK/SEQ numbers for the targeted subflow;
- valid address identifier for the malicious IP address used to hijack the connection;
However, this tool facilitates the attack procedure and avoid the ACK/SEQ number guessing. It actually sniffs the MPTCP packets between client and server at the beginning, manipulating the values from there. Moreover, the tool takes for granted that the attacker is also aware of the four-tuble (IP addresses and ports). The address identifier doesn't represent a particular problem in this case. ACK/SEQ values are the only data sniffed on the ongoing connection by this tool, but it is possible to elaborate a procedure to guess the above-mentioned numbers and carry out a 100% blind attack (even though the complexity of the attack would increase considerably).
- Another important note from RFC 7430:
" Note: In order to be able to successfully perform this attack, the attacker needs to be able to send packets with a forged source address. This means that the attacker cannot be located in a network where techniques like ingress filtering [RFC2827] or source address validation [RFC7039] are deployed. However, ingress filtering is not as widely implemented as one would expect and hence cannot be relied upon as a mitigation for this kind of attack. "
The Scapy script has been tested and tuned specifically to hijack a netcat communication and it is necessary to follow the steps in the guide carefully in order to achieve the desired result. Possible future work might allow higher flexibility for this tool.