CoreDataCodable contains protocols and extensions for making Core Data play nice with Swift's Codable protocols
- iOS 10+
- macOS 10.12+ (Sierra)
- Swift 4+
- Xcode 10.2
You want to add pod 'CoreDataCodable', '~> 1.0' similar to the following to your Podfile:
target 'MyApp' do
pod 'CoreDataCodable', '~> 1.0'
endThen run pod install inside your terminal, or from CocoaPods.app.
Alternatively to give it a test run, run the command:
$ pod try CoreDataCodableTo integrate CoreDataCodable into your Xcode project using Carthage, specify it in your Cartfile:
github "peterringset/CoreDataCodable" ~> 1.0
Then run carthage update inside your terminal.
To make an NSManagedObject-subclass be parsable through Decodable you can declare conformance to DecodableManagedObject, and implement the protocol:
import CoreData
import CoreDataCodable
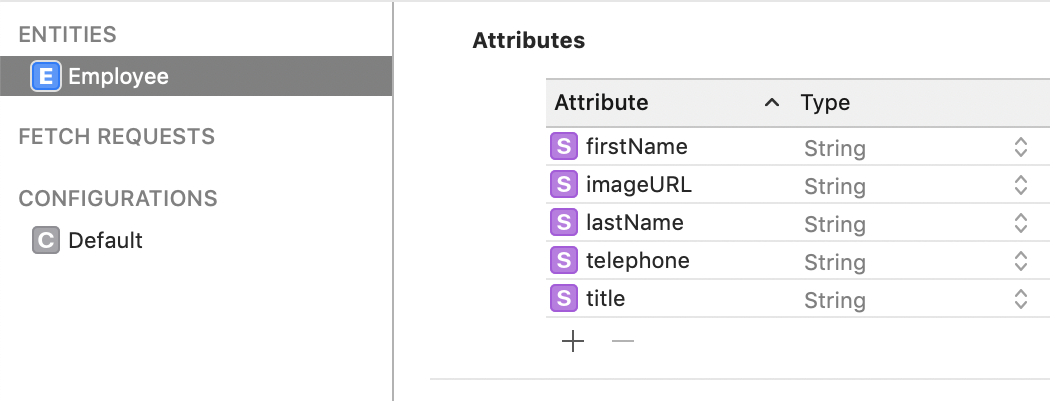
extension Employee: DecodableManagedObject {
public enum CodingKeys: String, CodingKey {
case firstName
case lastName
case title
case telephone
case imageURL
}
public func setValues(from decoder: Decoder) throws {
let container = try decoder.container(keyedBy: CodingKeys.self)
firstName = try container.decode(String.self, forKey: .firstName)
lastName = try container.decode(String.self, forKey: .lastName)
title = try container.decode(String.self, forKey: .title)
telephone = try container.decode(String.self, forKey: .telephone)
imageURL = try container.decode(String.self, forKey: .imageURL)
}
}To use this together with Swift's JSONDecoder, you have to assign a managed object context instance to the decoders userInfo:
let decoder = JSONDecoder()
decoder.userInfo[.managedObjectContext] = persistentContainer.newBackgroundContext()
let employees = try decoder.decode(Employee.self, from: json)This will insert the object into the provided context. Note that it is still up to you to save the context after parsing is done.
If you have an application where you will download entities that you already have in a local database, you can use ManagedObjectUpsert to help you manage that. This requires the entity class to conform to FetchableManagedObject, a protocol that tells us how to query the local database for an existing instance.
extension Employee {
public typealias FetchableCodingKeys = CodingKeys
public typealias Identifier = String
public static var identifierKey: Employee.CodingKeys {
return .lastName
}
}Then you can modify the decoding call to be
let upsert = try decoder.decode(ManagedObjectUpsert<Employee>.self, from: json)
let employee = upsert.objectThere is also a corresponding struct called ManagedObjectsUpsert for decoding an array of objects with the upsert mechanism.
CoreDataCodable is compatible with Core Data's codegen feature, but you should be aware that if you're using custom types (that are transformable), you will have to use the Manual/None alternatives. You can still get Xcode to generate the source for the entity, but you will have to regenerate the file(s) manually whenever you make changes to the object model. A good tip is to add customizations to the file named Entity+CoreDataClass.swift, that makes it easier whenever you need to regenerate the entity code.
import Foundation
import CoreData
import CoreDataCodable
@objc(Entity)
public class Entity: NSManagedObject {
}
extension Entity {
enum CodingKeys: String, CodingKey {
case name
case url
}
public func setValues(from decoder: Decoder) throws {
let container = try decoder.container(keyedBy: CodingKeys.self)
name = try container.decode(String.self, forKey: .name)
url = try container.decode(URL.self, forKey: .url)
}
}