Screened Poisson Surface Reconstruction
(and Smoothed Signed Distance Reconstruction)
Version 9.01
links
executables
usage
changes
support
LINKS
-
Papers:
[Kazhdan, Bolitho, and Hoppe, 2006],
[Calakli and Taubin, 2011],
[Kazhdan and Hoppe, 2013]
Executables: Win64
Source Code: ZIP GitHub
Older Versions: V9.0, V8.0, V7.0, V6.13a, V6.13, V6.12, V6.11, V6.1, V6, V5.71, V5.6, V5.5a, V5.1, V5, V4.51, V4.5, V4, V3, V2, V1
EXECUTABLES
- --in <input points>
- This string is the name of the file from which the point set will be read.
If the file extension is .ply, the file should be in PLY format, giving the list of oriented vertices with the x-, y-, and z-coordinates of the positions encoded by the properties x, y, and z and the x-, y-, and z-coordinates of the normals encoded by the properties nx, ny, and nz .
If the file extension is .bnpts, the file should be a binary file, consisting of blocks of 6 32-bit floats: x-, y-, and z-coordinates of the point's position, followed by the x-, y-, and z-coordinates of the point's normal. (No information about the number of oriented point samples should be specified.)
Otherwise, the file should be an ascii file with groups of 6, white space delimited, numbers: x-, y-, and z-coordinates of the point's position, followed by the x-, y- and z-coordinates of the point's normal. (No information about the number of oriented point samples should be specified.)
- [--out <output triangle mesh>]
- This string is the name of the file to which the triangle mesh will be written. The file is written in PLY format.
- [--voxel <output voxel grid>]
- This string is the name of the file to which the sampled implicit function will be written. The filw is wrtten out in binary, with the first 4 bytes corresponding to the (integer) sampling resolution, 2^d, and the next 4 x 2^d x 2^d x 2^d bytes corresponding to the (single precision) floating point values of the implicit function.
- [--degree <B-spline degree>]
- This integer specifies the degree of the B-spline that is to be used to define the finite elements system.
Larger degrees support higher order approximations, but come at the cost of denser system matrices (incurring a cost in both space and time).
The default value for this parameter is 2. - [--bType <boundary type>]
- This integer specifies the boundary type for the finite elements. Valid values are:
- 1: Free boundary constraints
- 2: Dirichlet boundary constraints
- 3: Neumann boundary constraints
- [--depth <reconstruction depth>]
- This integer is the maximum depth of the tree that will be used for surface reconstruction.
Running at depth d corresponds to solving on a voxel grid whose resolution is no larger than
2^d x 2^d x 2^d. Note that since the reconstructor adapts the octree to the
sampling density, the specified reconstruction depth is only an upper bound.
The default value for this parameter is 8. - [--scale <scale factor>]
- This floating point value specifies the ratio between the diameter of the cube used for reconstruction
and the diameter of the samples' bounding cube.
The default value is 1.1. - [--samplesPerNode <minimum number of samples>]
- This floating point value specifies the minimum number of sample points that should fall within an
octree node as the octree construction is adapted to sampling density. For noise-free samples, small values
in the range [1.0 - 5.0] can be used. For more noisy samples, larger values in the range [15.0 - 20.0] may
be needed to provide a smoother, noise-reduced, reconstruction.
The default value is 1.0. - [--pointWeight <interpolation weight>]
- This floating point value specifies the importance that interpolation of the point samples
is given in the formulation of the screened Poisson equation.
The results of the original (unscreened) Poisson Reconstruction can be obtained by setting this value to 0.
The default value for this parameter is 4. - [--confidence]
- Enabling this flag tells the reconstructor to use the size of the normals as confidence information. When the flag is not enabled, all normals are normalized to have unit-length prior to reconstruction.
- [--nWeights]
- Enabling this flag tells the reconstructor to use the size of the normals to modulate the interpolation weights. When the flag is not enabled, all points are given the same weight.
- [--iters <GS iters>]
- This integer value specifies the number of Gauss-Seidel relaxations to be performed at each level of the hiearchy.
The default value for this parameter is 8. - [--cgDepth <conjugate gradients solver depth>]
- This integer is the depth up to which a conjugate-gradients solver will be used to solve the linear system. Beyond this depth Gauss-Seidel relaxation will be used.
The default value for this parameter is 0. - [--fullDepth <adaptive octree depth>]
- This integer specifies the depth beyond depth the octree will be adapted.
At coarser depths, the octree will be complete, containing all 2^d x 2^d x 2^d nodes.
The default value for this parameter is 5. - [--voxelDepth <voxel sampling depth>]
- This integer is the depth of the regular grid over which the implicit function is to be sampled.
Running at depth d corresponds to sampling on a voxel grid whose resolution is 2^d x 2^d x 2^d.
The default value for this parameter is the value of the --depth parameter. - [--primalVoxel]
- Enabling this flag when outputing to a voxel file has the reconstructor sample the implicit function at the corners of the grid, rather than the centers of the cells.
- [--color <pull factor>]
- If specified, the reconstruction code assumes that the input is equipped with colors and will extrapolate the color values to the vertices of the reconstructed mesh. The floating point value specifies the relative importance of finer color estimates over lower ones. (In practice, we have found that a pull factor of 16 works well.)
- [--density]
- Enabling this flag tells the reconstructor to output the estimated depth values of the iso-surface vertices.
- [--linearFit]
- Enabling this flag has the reconstructor use linear interpolation to estimate the positions of iso-vertices.
- [--polygonMesh]
- Enabling this flag tells the reconstructor to output a polygon mesh (rather than triangulating the results of Marching Cubes).
- [--threads <number of processing threads>]
- This integer specifies the number of threads across which the reconstruction
algorithm should be parallelized.
The default value for this parameter is equal to the numer of (virtual) processors on the executing machine. - [--verbose]
- Enabling this flag provides a more verbose description of the running times and memory usages of individual components of the surface reconstructor.
-
PoissonRecon
- --in <input points>
- This string is the name of the file from which the point set will be read.
If the file extension is .ply, the file should be in PLY format, giving the list of oriented vertices with the x-, y-, and z-coordinates of the positions encoded by the properties x, y, and z and the x-, y-, and z-coordinates of the normals encoded by the properties nx, ny, and nz .
If the file extension is .bnpts, the file should be a binary file, consisting of blocks of 6 32-bit floats: x-, y-, and z-coordinates of the point's position, followed by the x-, y-, and z-coordinates of the point's normal. (No information about the number of oriented point samples should be specified.)
Otherwise, the file should be an ascii file with groups of 6, white space delimited, numbers: x-, y-, and z-coordinates of the point's position, followed by the x-, y- and z-coordinates of the point's normal. (No information about the number of oriented point samples should be specified.)
- [--out <output triangle mesh>]
- This string is the name of the file to which the triangle mesh will be written. The file is written in PLY format.
- [--voxel <output voxel grid>]
- This string is the name of the file to which the sampled implicit function will be written. The filw is wrtten out in binary, with the first 4 bytes corresponding to the (integer) sampling resolution, 2^d, and the next 4 x 2^d x 2^d x 2^d bytes corresponding to the (single precision) floating point values of the implicit function.
- [--degree <B-spline degree>]
- This integer specifies the degree of the B-spline that is to be used to define the finite elements system.
Larger degrees support higher order approximations, but come at the cost of denser system matrices (incurring a cost in both space and time).
The default value for this parameter is 2. - [--depth <reconstruction depth>]
- This integer is the maximum depth of the tree that will be used for surface reconstruction.
Running at depth d corresponds to solving on a voxel grid whose resolution is no larger than
2^d x 2^d x 2^d. Note that since the reconstructor adapts the octree to the
sampling density, the specified reconstruction depth is only an upper bound.
The default value for this parameter is 8. - [--scale <scale factor>]
- This floating point value specifies the ratio between the diameter of the cube used for reconstruction
and the diameter of the samples' bounding cube.
The default value is 1.1. - [--samplesPerNode <minimum number of samples>]
- This floating point value specifies the minimum number of sample points that should fall within an
octree node as the octree construction is adapted to sampling density. For noise-free samples, small values
in the range [1.0 - 5.0] can be used. For more noisy samples, larger values in the range [15.0 - 20.0] may
be needed to provide a smoother, noise-reduced, reconstruction.
The default value is 1.0. - [--valueWeight <zero-crossing interpolation weight>]
- This floating point value specifies the importance that interpolation of the point samples
is given in the formulation of the screened Smoothed Signed Distance Reconstruction.
The default value for this parameter is 4. - [--gradientWeight <normal interpolation weight>]
- This floating point value specifies the importance that interpolation of the points' normals
is given in the formulation of the screened Smoothed Signed Distance Reconstruction.
The default value for this parameter is 0.001. - [--biLapWeight <bi-Laplacian weight weight>]
- This floating point value specifies the importance that the bi-Laplacian regularization
is given in the formulation of the screened Smoothed Signed Distance Reconstruction.
The default value for this parameter is 0.00001. - [--confidence]
- Enabling this flag tells the reconstructor to use the size of the normals as confidence information. When the flag is not enabled, all normals are normalized to have unit-length prior to reconstruction.
- [--nWeights]
- Enabling this flag tells the reconstructor to use the size of the normals to modulate the interpolation weights. When the flag is not enabled, all points are given the same weight.
- [--iters <GS iters>]
- This integer value specifies the number of Gauss-Seidel relaxations to be performed at each level of the hiearchy.
The default value for this parameter is 8. - [--cgDepth <conjugate gradients solver depth>]
- This integer is the depth up to which a conjugate-gradients solver will be used to solve the linear system. Beyond this depth Gauss-Seidel relaxation will be used.
The default value for this parameter is 0. - [--fullDepth <adaptive octree depth>]
- This integer specifies the depth beyond depth the octree will be adapted.
At coarser depths, the octree will be complete, containing all 2^d x 2^d x 2^d nodes.
The default value for this parameter is 5. - [--voxelDepth <voxel sampling depth>]
- This integer is the depth of the regular grid over which the implicit function is to be sampled.
Running at depth d corresponds to sampling on a voxel grid whose resolution is 2^d x 2^d x 2^d.
The default value for this parameter is the value of the --depth parameter. - [--primalVoxel]
- Enabling this flag when outputing to a voxel file has the reconstructor sample the implicit function at the corners of the grid, rather than the centers of the cells.
- [--color <pull factor>]
- If specified, the reconstruction code assumes that the input is equipped with colors and will extrapolate the color values to the vertices of the reconstructed mesh. The floating point value specifies the relative importance of finer color estimates over lower ones. (In practice, we have found that a pull factor of 16 works well.)
- [--density]
- Enabling this flag tells the reconstructor to output the estimated depth values of the iso-surface vertices.
- [--nonLinearFit]
- Enabling this flag has the reconstructor use quadratic interpolation to estimate the positions of iso-vertices.
- [--polygonMesh]
- Enabling this flag tells the reconstructor to output a polygon mesh (rather than triangulating the results of Marching Cubes).
- [--threads <number of processing threads>]
- This integer specifies the number of threads across which the reconstruction
algorithm should be parallelized.
The default value for this parameter is equal to the numer of (virtual) processors on the executing machine. - [--verbose]
- Enabling this flag provides a more verbose description of the running times and memory usages of individual components of the surface reconstructor.
-
SSDRecon
- --in <input triangle mesh>
- This string is the name of the file from which the triangle mesh will be read. The file is read in PLY format and it is assumed that the vertices have a value field which stores the signal's value. (When run with --density flag, the reconstructor will output this field with the mesh vertices.)
- --trim <trimming value>
- This floating point values specifies the value for mesh trimming. The subset of the mesh with signal value less than the trim value is discarded.
- [--out <output triangle mesh>]
- This string is the name of the file to which the triangle mesh will be written. The file is written in PLY format.
- [--smooth <smoothing iterations>]
- This integer values the number of umbrella smoothing operations to perform on the signal before trimming.
The default value is 5. - [--aRatio <island area ratio>]
- This floating point value specifies the area ratio that defines a disconnected component as an "island". Connected components whose area, relative to the total area of the mesh, are smaller than this value will be merged into the output surface to close small holes, and will be discarded from the output surface to remove small disconnected components.
The default value 0.001. - [--polygonMesh]
- Enabling this flag tells the trimmer to output a polygon mesh (rather than triangulating the trimming results).
-
SurfaceTrimmer
USAGE
For testing purposes, three point sets are provided:
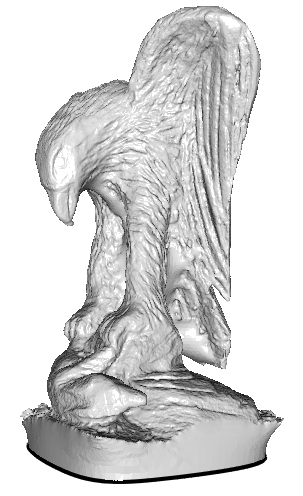
- Eagle:
A set of 796,825 oriented point samples with color (represented in PLY format) was obtained in the EPFL Scanning 3D Statues from Photos course.
- The original Poisson Reconstruction algorithm can be invoked by calling:
using the --pointWeight 0 argument to disable the screening.% PoissonRecon --in eagle.points.ply --out eagle.unscreened.ply --depth 10 --pointWeight 0
- By default, screening is enabled so the call:
produces a reconstruction that more faithfully fits the input point positions.% PoissonRecon --in eagle.points.ply --out eagle.screened.ply --depth 10
- A reconstruction of the eagle that extrapolates the color values from the input samples can be obtained by calling:
using the --color 16 to indicate both that color should be used, and the extent to which finer color estimates should be preferenced over coarser estimates.% PoissonRecon --in eagle.points.ply --out eagle.screened.color.ply --depth 10 --color 16 - Finally, a reconstruction the eagle that does not close up the holes can be obtained by first calling:
using the --density flag to indicate that density estimates should be output with the vertices of the mesh, and then calling:% PoissonRecon --in eagle.points.ply --out eagle.screened.color.ply --depth 10 --color 16 --density
to remove all subsets of the surface where the sampling density corresponds to a depth smaller than 7.% SurfaceTrimmer --in eagle.screened.color.ply --out eagle.screened.color.trimmed.ply --trim 7
Unscreened Screened Screened + Color Screened + Color + Trimmed - The original Poisson Reconstruction algorithm can be invoked by calling:
- Bunny:
A set of 362,271 oriented point samples (represented in PLY format) was obtained by merging the data from the original Stanford Bunny
range scans. The orientation of the sample points was estimated
using the connectivity information within individual range scans.
The surface of the model can be reconstructed by calling the surface reconstructor as follows:% PoissonRecon --in bunny.points.ply --out bunny.ply --depth 10 - Horse:
A set of 100,000 oriented point samples (represented in ASCII format) was obtained by sampling a virtual horse model with a sampling density proportional to curvature, giving a set of non-uniformly distributed points.
The surface of the model can be reconstructed by calling the surface reconstructor as follows:% PoissonRecon --in horse.npts --out horse.ply --depth 10
To convert the binary PLY format to
Hugues Hoppe's ASCII
mesh format, a Perl script is provided.
As an examples, the reconstructed bunny can be converted into the ASCII mesh format as follows:
% ply2mesh.pl bunny.ply > bunny.mCHANGES
Version 3:
- The implementation of the --samplesPerNode parameter has been modified so that a value of "1" more closely corresponds to a distribution with one sample per leaf node.
- The code has been modified to support compilation under MSVC 2010 and the associated solution and project files are now provided. (Due to a bug in the Visual Studios compiler, this required modifying the implementation of some of the bit-shifting operators.)
- The code supports screened reconstruction, with interpolation weight specified through the --pointWeight parameter.
- The code has been implemented to support parallel processing, with the number of threads used for parallelization specified by the --threads parameter.
- The input point set can now also be in PLY format, and the file-type is determined by the extension, so that the --binary flag is now obsolete.
- At depths coarser than the one specified by the value --minDepth the octree is no longer adaptive but rather complete, simplifying the prolongation operator.
- The algorithmic complexity of the solver was reduced from log-linear to linear.
- Smart pointers were added to ensure that memory accesses were in bounds.
- The --density flag was added to the reconstructor to output the estimated depth of the iso-vertices.
- The SurfaceTrimmer executable was added to support trimming off the subset of the reconstructed surface that are far away from the input samples, thereby allowing for the generation of non-water-tight surface.
- Minor bug-fix to address incorrect neighborhood estimation in the octree finalization.
- Modified to support depths greater than 14. (Should work up to 18 or 19 now.)
- Improved speed and memory performance by removing the construction of integral and value tables.
- Fixed a bug in Version 5.5 that used memory and took more time without doing anything useful.
- Added the --normalWeight flag to support setting a point's interpolation weight in proportion to the magnitude of its normal.
- Modified the setting of the constraints, replacing the map/reduce implementation with OpenMP atomics to reduce memory usage.
- Fixed bugs that caused numerical overflow when processing large point clouds on multi-core machines.
- Improved efficiency of the iso-surface extraction phse.
- Added the function GetSolutionValue to support the evaluation of the implicit function at a specific point.
- Modified the solver to use Gauss-Seidel relaxation instead of conjugate-gradients at finer resolution.
- Re-ordered the implementation of the solver so that only a windowed subset of the matrix is in memory at any time, thereby reducing the memory usage during the solver phase.
- Separated the storage of the data associated with the octree nodes from the topology.
- Re-ordered the implementation of the iso-surface extraction so that only a windowed subset of the octree is in memory at any time, thereby reducing the memory usage during the extracted phase.
- Fixed a bug that created a crash in the evaluation phase when --pointWeight is set zero.
- Removed the OpenMP firstprivate directive as it seemed to cause trouble under Linux compilations.
- Added a MemoryPointStream class in PointStream.inl to support in-memory point clouds.
- Modified the signature of Octree::SetTree in MultiGridOctreeData.h to take in a pointer to an object of type PointStream rather than a file-name.
- Modified the signature of Octree::SetIsoSurface to rerun a void. [cloudcompare]
- Added a definition of SetIsoVertexValue supporting double precision vertices. [cloudcompare]
- Removed Time.[h/cpp] from the repository. [cloudcompare/asmaloney]
- Fixed assignment bug in Octree::SetSliceIsoVertices. [asmaloney]
- Fixed initialization bug in SortedTreeNodes::SliceTableData and SortedTreeNodes::XSliceTableData. [asmaloney]
- Included stdlib.h in Geometry.h. [asmaloney]
- Fixed default value bug in declaration of Octree::SetTree. [asmaloney]
- Added functionality to support color extrapolation if present in the input.
- Modified a bug with the way in which sample contributions were scaled.
- Added support for different degree B-splines. (Note that as the B-spline degree is a template parameter, only degree 1 through 4 are supported. If higher order degrees are desired, additional template parameters can be easily added in the body of the Execute function inside of PoissonRecon.cpp. Similarly, to reduce compilation times, support for specific degrees can be removed.)
- Added the --primalVoxel flag to support to extraction of a voxel grid using primal sampling.
- Changed the implementation of the voxel sampling so that computation is now linear, rather than log-linear, in the number of samples.
- Added support for free boundary conditions.
- Extended the solver to support more general linear systems. This makes it possible to use the same framework to implement the Smoothed Signed Distance Reconstruction of Calakli and Taubin (2011).
- Modified the implementation of density estimation and input representation. This tends to define a slightly larger system. On its own, this results in slightly increased running-time/footprint for full-res reconstructions, but provides a substantially faster implementation when the output complexity is smaller than the input.
- Reverted the density estimation to behave as in Version 8.0.
SUPPORT
This work genersouly supported by NSF grants #0746039 and #1422325.
HOME