A full list of the existing solutions can be found here.
- https://www.notion.so/atlanhq/The-Ultimate-Repository-of-Data-Discovery-Solutions-149b0ea2a2ed401d84f2b71681c5a369
- https://medium.com/work-bench/work-bench-snapshot-the-evolution-of-data-discovery-catalog-2f6c0425616b
As we can only use open source solution. So our possible candidates are:
- Atlas
- Amundsen
- DataHub
- Marquez (Not tested yet)
If you are not familliar with the terminology such as data governance, data management and metadata management. Please go to this page
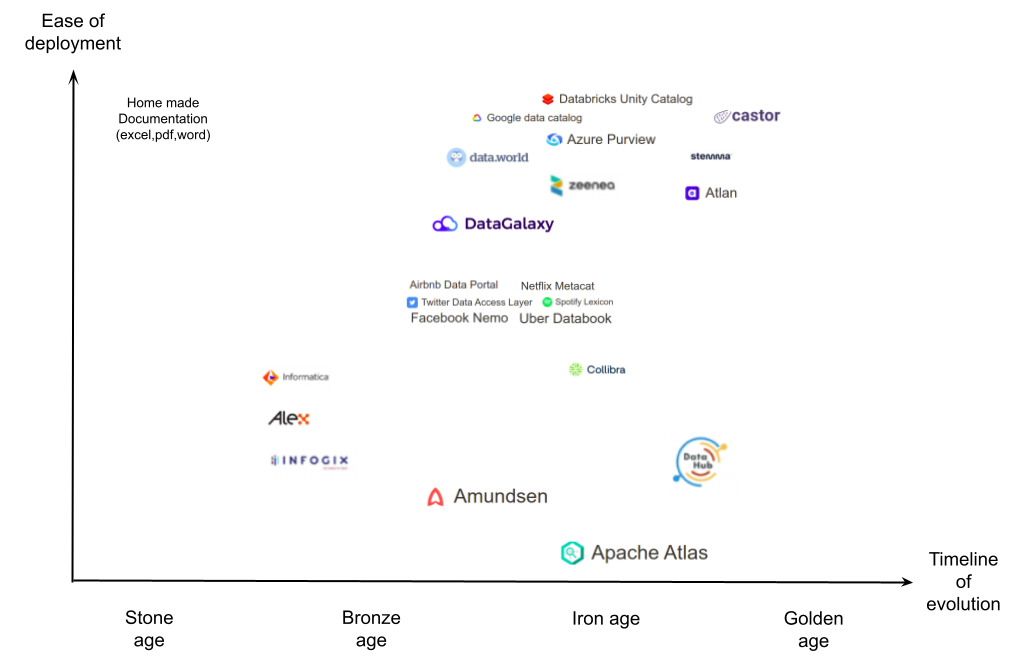
Below figure shows a classification of the existing solutions
- Stone age: No software, people use pdf, excel, or other documents to describe the data. Everything is done manually.
- Bronze age: Basic software with a relational database, similar to Excel, but provides a web interface that allows you to ingest/update metadata.
- Iron age: software designed to help the data professionals in collecting metadata automatically and managing them.
- Golden age: allow all users(e.g. business users, data professionals) to contribute to the metadata ingestion in a collaborative and painless way. Data professionals can easily audit the metadata modification(e.g. accept or reject). Business users can require new metadata features of data(e.g. new data quality criteria, more attributes of a data description)
To choose the right tool/solution for your organization, you need to follow below steps:
The first thing to do is to understand your exact need, and narrow your scope down. There is no magical tool that can resolve all your requirements.
-
Do I need a data governance tool to help me to define the policies and metrics?
-
Do I need a Data validation tool to do data quality control?
-
Do I need a metadata management tool to catalog data and do data discovery, data lineage?
Once you have defined your scope, you need to identify the top pain points that affect your data productivity. For each pain point, you need to add a severity(e.g. 1-10).
For example, if your data scientist or analyst spend lots of their time on finding the data of interest, you should put this pain point finding data of interest with a severity 10.
After identifying the pain points, we need to provide a solution for each pain point. Then we need to define detailed requirements for each solution. Based on the severity of the pain points, we should associate a priority to the solution implementation.
For example, for finding the data of interest, we need to provide a data catalog/discovery service. This data catalog service should:
- contain a metadata store to store all types of metadata(e.g. intra, inter, global)
- provide a search engine to find data easily by using
- data description (e.g format, owner, creation date, etc),
- semantic description (e.g taxonomy, thesaurus, etc.)
- data relation (e.g. lineage, grouping)
In previous section, we have defined all functional requirements. To evaluate a tool, we also need to define non-functional requirements such as cost of deployment, maintenance, security (of the tool). You should talk with the data professionals to define these non-functional requirements.
Now we need to define the benchmark metric based on all the requirements (e.g. functional and non-functional).
Now we need to evaluate the existing tools by using the metrics that we have defined . Base on the score of each tool, we should know which tool is the best solution for your organization.
We narrowed our scope to metadata management. So we will not address problems such as data validation, security, etc. If you are not familial with the five domains of the data management, please visit this page
| Id | pain_point | severity (0~10) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hard to find the data of interest | 10 |
| 2 | Not knowing the data provider name | 10 |
| 3 | Not knowing the data provenance | 8 |
| 4 | Not knowing the data schema | 9 |
| 5 | Not knowing who and when of the data modification | 7 |
| 6 | Not knowing data are duplicated or not | 5 |
Based on the identified pain points, we will propose two solutions
The data description service should provide a metadata store that can store:
- customizable data description (intra-metadata) such as data provider name, data schema, data format, data size, etc. For pain point 2, 4, 5
- relationships between data (inter-metadata) such as lineage, tagging and grouping. For pain point 3,6
- semantic metadata (global-metadata) such as thesaurus, taxonomy, etc. For pain point 1
It should also provide user-friendly interface to allow user to visualize the data description It should also provide user-friendly interface to allow user to associate data with semantic metadata
The data discovery service should provide a search engine that can find data:
- by using data description such as data provider name, data schema, data format, data size, etc.
- by using semantic metadata
It should also provide user-friendly interface to allow user to visualize the data lineage
We can summarize the functional requirements into below metrics:
- customizable_data_description(Boolean): If it allows users to customize attributes to describe data
- data_description_visu(Boolean): If it allows users to visualize attributes of a data easily.
- grouping_metadata(Boolean): If it allows users to define groups(e.g. organization, year, security_level, etc.) and associate any data to any group.
- semantic_metadata(Boolean): If it allows users to define semantic metadata (e.g. thesaurus, taxonomy, etc.) and associate any data to them
- lineage_metadata(Boolean): If it allows users to define lineage metadata (e.g. source of a join table, result table of a transformation, etc.) and visualize them.
- search_by_description(Boolean): If it allows users to search data by using the data description (e.g. owner, format, creation_data, etc.)
- search_by_semantic(Boolean): If it allows users to search data by using the semantic metadata
- search_by_lineage(Boolean): If it allows users to search data by using their lineage
We also need to define non-functional requirements:
-
ease_of_deployment(Cat:easy->1, median->0, hard->-1): If it is difficult to deploy and maintain.
-
capacity (Cat:small->0, median->1, large->2): how many data entity can the tool handle (e.g. store and search)? small: 0-500k, median: 500k-1 million, large: > 1 million.
-
metadata_ingestion_method(String) : list the supported metadata ingestion method
-
data_access(Boolean): If it allows users to access data directly.
-
catalog_external_data(Boolean): if it allows users to catalog public or third party data that are stored outside the organization.
-
supported_data_type(String): List all data type that the tool can catalog.
-
lineage_granularity_level(String): List the granularity level that a lineage can do.
-
collaboration(Boolean): If it allows business user and data professionals to work together to enrich the metadata.
-
metadata_audit_log: If it has audit log(creation, modification, deletion) for metadata.
-
usage_metrics: If it provides platform activity metrics(e.g. user id, search query, etc. )
-
access_control(Cat:basic->0, median->1, advance->2): If it allows access control on reading and writing metadata. basic means grant rights or not, no RBAC support. Median means has RBAC support, but RBAC rule does not have the granularity to control individual entity. Advance means has RBAC and granular access control.
-
authentication_method(String): List all supported authentication method.
| tool_name | customizable_data_description | data_description_visu | grouping_metadata | lineage_metadata | semantic_metadata | score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amundsen | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | 2 |
| Atlas | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 5 |
| Datahub | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes* | Yes | 5 |
| tool_name | search_by_description | search_by_semantic | search_by_lineage | ease_of_deployment | capacity | score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amundsen | Yes* | No | No | median | median | 1.5 |
| Atlas | Yes | Yes | Yes | hard | large | 4 |
| Datahub | No | Yes | Yes* | hard | large | 2.5 |
| tool_name | metadata_ingestion_method | data_access | catalog_external_data | supported_data_type | collaboration | score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amundsen | Python API | No | Yes | DB, table, column | No | 3 |
| Atlas | Python/Java/Rest API, Web UI, automated Hook | No | Yes | All | No | 5 |
| Datahub | Python Client(YAML config), Rest API | No | Yes | All | No | 4.5 |
| tool_name | metadata_audit_log | usage_metrics | access_control | authentication_method | score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amundsen | No | No | basic | OIDC | 1 |
| Atlas | Yes | No | median | OIDC,file,Kerberos,ldap,PAM | 4 |
| Datahub | No | Yes | advance | OIDC,JAAS(file,db,ldap) | 5 |
| tool_name | Total_score |
|---|---|
| Amundsen | 7.5 |
| Atlas | 18 |
| Datahub | 17 |
Note :
- Amundsen provides search by description, but only allow five description types: source type(data type), column_name, etc. Unlike Atlas user can use all description to filter data.
- Datahub provides lineage metadata, but they collect the lineage metadata only for task lineage. So we don't have all the information about produced data. As a result, we can't really search a data by lineage.