jermp / 2i_bench Goto Github PK
View Code? Open in Web Editor NEWA C++ library to benchmark inverted indexes.
License: MIT License
A C++ library to benchmark inverted indexes.
License: MIT License
I used Boost version 1.83.0 in this project, but it seems to have encountered many compilation errors. So, I'm wondering which version of Boost I should use to reproduce the results in the paper.
This is a proposal for encoding inverted index integer sequences using a number system based on binomial coefficients.
This number system is chosen because the minimum number of bits needed to encode a list of strictly increasing integers
is given by the equation 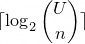
where 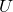 is largest number in the list and
is largest number in the list and 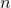 is the number of elements in the list.
is the number of elements in the list.
For example to encode the sequence 1,2,3,4,10,11 we need at least 9 bits: 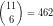 and
and
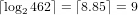 .
.
Binary interpolative coding, one of the best methods for inverted list compression takes at least 20 bits to represent the example sequence. You can confirm this here.
However, if we represent the same sequence as a sum of binomial coefficients, it takes 10 bits to encode the list, and an extra 3 bits to store the length of the list. The total is 13 bits. You can confirm this here.
Compression is a solved problem. The best compressors work by changing radixes, or number bases to find the most concise representation of data.
For instance, arithmetic coding is a generalized change of radix for coding
at the information theoretic entropy bound. This bound is a measure of redundancy - how many duplicates are in your data. Strictly increasing integer sequences have no duplicates, therefore, cannot be compressed
according to the information theoretic bound. This means huffman coding and arithmetic coding methods are inefficient with non-repetitive integer sequences.
This rfc proposes the use of the combinatorial number system to encode inverted index integer sequences at the combinatorial information theoretic entropy bound.
Just like arithmetic coding, this change in number systems allows us to encode integer sequences with the least number of bits.
I am a Math major in my junior year and if this RFC succeeds I would love to take a gap year and work on this library full time. The library
has sample code for converting between binary and the combinatorial number system using a greedy algorithm, or by generating a lookup table.
Any natural number 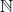 can be uniquely written as a sum of binomial coefficients
can be uniquely written as a sum of binomial coefficients
using this greedy algorithm.
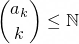
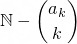
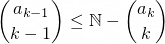
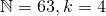
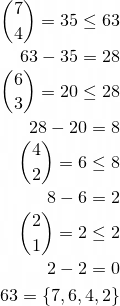
To reverse the process, sum your list of binomial coefficients
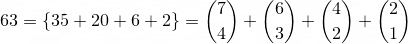
In the example above, it can be seen that the sequence 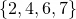
can be encoded in 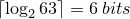 using the combinatorial number system with an extra 3 bits to store the length of the sequence. This is a total of 9 bits to encode this sequence.
using the combinatorial number system with an extra 3 bits to store the length of the sequence. This is a total of 9 bits to encode this sequence.
Using this library it can be confirmed that binary interpolative coding takes between 15 to 23 bits to encode the same sequence.
This is a screenshot of the result of binary interpolative coding.
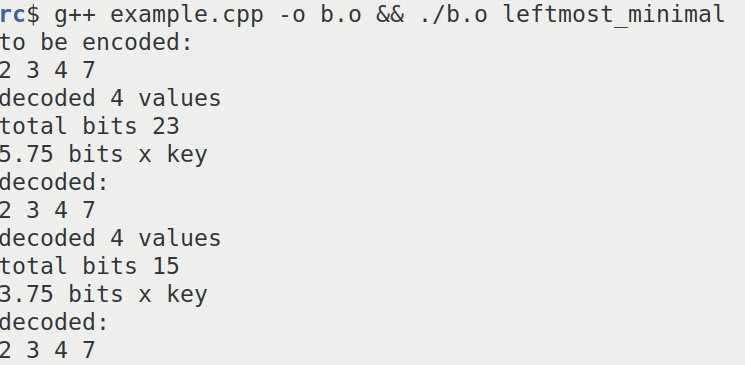
The combinatorial number systems always encodes integer sequences at the entropy limit.
A declarative, efficient, and flexible JavaScript library for building user interfaces.
🖖 Vue.js is a progressive, incrementally-adoptable JavaScript framework for building UI on the web.
TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript that compiles to clean JavaScript output.
An Open Source Machine Learning Framework for Everyone
The Web framework for perfectionists with deadlines.
A PHP framework for web artisans
Bring data to life with SVG, Canvas and HTML. 📊📈🎉
JavaScript (JS) is a lightweight interpreted programming language with first-class functions.
Some thing interesting about web. New door for the world.
A server is a program made to process requests and deliver data to clients.
Machine learning is a way of modeling and interpreting data that allows a piece of software to respond intelligently.
Some thing interesting about visualization, use data art
Some thing interesting about game, make everyone happy.
We are working to build community through open source technology. NB: members must have two-factor auth.
Open source projects and samples from Microsoft.
Google ❤️ Open Source for everyone.
Alibaba Open Source for everyone
Data-Driven Documents codes.
China tencent open source team.