SQLite3 Native Plugin for React Native for both Android (Classic and Native) and iOS
Inspired by fantastic work done by Chris Brody I did not want to re-invent the wheel. The original Cordova plugin was written so well and adhered to latest WebSQL API that there was no need to come up with anything much different. So the Cordova plugin was ported to React Native.
Features:
- iOS and Android supported via identical JavaScript API.
- Android in pure Java and Native modes
- SQL transactions
- JavaScript interface via plain callbacks or Promises.
- Pre-populated SQLite database import from application sandbox
Please let me know your projects that use these SQLite React Native modules. I will list them in the reference section. If there are any features that you think would benefit this library please post them.
The library had been developed for React 14 using XCode 6. It has been tested with React 0.21.0 and XCode 7 - it works fine out of the box without any need for tweaks or code changes. For XCode 7 the only difference is that sqlite ios library name suffix is tbd instead of dylib.
#Version History
v2.1.4 - tested with React 0.21.0
- Expose a bulk data retrieval interface from JS
- Fix JS 'strict' mode execution errors
v2.1.3
- Fix the runtime error in reflection.
v2.1.2
- Android Native SQLite connectivity
- Change how React parameters are processed to map a Number to Java Double
- Implent hooks for activity lifecycle and automatic db closing on destroy
- Fix How To Get Started instructions for Android
v2.1.1 - Fixes issues with XCode path and React Native version compatibility
v2.1 - Android support
v2.0 - Full support for Promise API. Backward compatible with Callbacks.
v1.0 - Intial release for iOS with full support of all operations based on plan JavaScript callbacks.
#How to use (iOS):
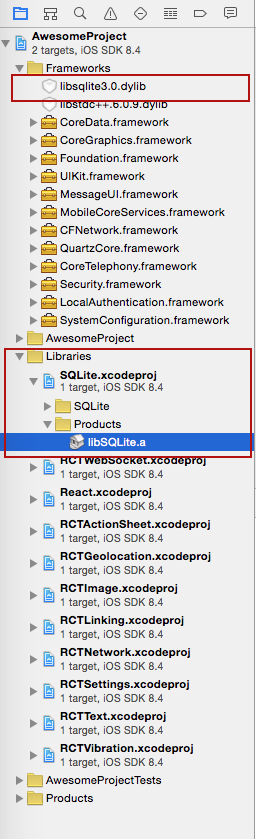
npm install --save react-native-sqlite-storageDrag the SQLite Xcode project as a dependency project into your React Native XCode project
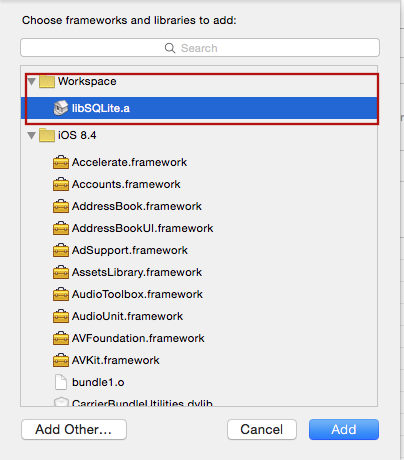
Add libSQLite.a (from Workspace location) to the required Libraries and Frameworks. Also add sqlite3.0.tbd (XCode 7) or libsqlite3.0.dylib (XCode 6 and earlier) in the same fashion using Required Libraries view (Do not just add them manually as the build paths will not be properly set)
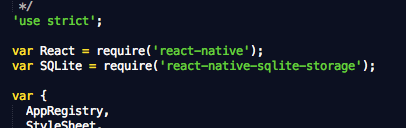
Add var SQLite = require('react-native-sqlite-storage') to your index.ios.js
Add JS application code to use SQLite API in your index.ios.js etc. Here is some sample code. For full working example see test/index.ios.callback.js. Please note that Promise based API is now supported as well with full examples in the working React Native app under test/index.ios.promise.js
errorCB(err) {
console.log("SQL Error: " + err);
},
successCB() {
console.log("SQL executed fine");
},
openCB() {
console.log("Database OPENED");
},
var db = SQLite.openDatabase("test.db", "1.0", "Test Database", 200000, openCB, errorCB);
db.transaction((tx) => {
tx.executeSql('SELECT * FROM Employees a, Departments b WHERE a.department = b.department_id', [], (tx, results) => {
console.log("Query completed");
// Get rows with Web SQL Database spec compliance.
var len = results.rows.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
let row = results.rows.item(i);
console.log(`Employee name: ${row.name}, Dept Name: ${row.deptName}`);
}
// Alternatively, you can use the non-standard raw method.
/*
let rows = results.rows.raw(); // shallow copy of rows Array
rows.map(row => console.log(`Employee name: ${row.name}, Dept Name: ${row.deptName}`));
*/
});
});#How to use (Android):
npm install --save react-native-sqlite-storage// file: android/settings.gradle
...
include ':react-native-sqlite-storage'
project(':react-native-sqlite-storage').projectDir = new File(rootProject.projectDir, '../node_modules/react-native-sqlite-storage/src/android')// file: android/app/build.gradle
...
dependencies {
...
compile project(':react-native-sqlite-storage')
}Step 4 - Register React Package (this should work on React version but if it does not , try the ReactActivity based approach
...
import org.pgsqlite.SQLitePluginPackage;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements DefaultHardwareBackBtnHandler {
private ReactInstanceManager mReactInstanceManager;
private ReactRootView mReactRootView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
mReactRootView = new ReactRootView(this);
mReactInstanceManager = ReactInstanceManager.builder()
.setApplication(getApplication())
.setBundleAssetName("index.android.bundle") // this is dependant on how you name you JS files, example assumes index.android.js
.setJSMainModuleName("index.android") // this is dependant on how you name you JS files, example assumes index.android.js
.addPackage(new MainReactPackage())
.addPackage(new SQLitePluginPackage(this)) // register SQLite Plugin here
.setUseDeveloperSupport(BuildConfig.DEBUG)
.setInitialLifecycleState(LifecycleState.RESUMED)
.build();
mReactRootView.startReactApplication(mReactInstanceManager, "AwesomeProject", null); //change "AwesomeProject" to name of your app
setContentView(mReactRootView);
}
...Alternative approach on newer versions of React Native (0.18+):
import org.pgsqlite.SQLitePluginPackage;
public class MainActivity extends ReactActivity {
......
/**
* A list of packages used by the app. If the app uses additional views
* or modules besides the default ones, add more packages here.
*/
@Override
protected List<ReactPackage> getPackages() {
return Arrays.<ReactPackage>asList(
new SQLitePluginPackage(this)) // register SQLite Plugin here
new MainReactPackage());
}
}Step 5 - Require and use in Javascript - see full examples (callbacks and Promise) in test directory.
// file: index.android.js
var React = require('react-native');
var SQLite = require('react-native-sqlite-storage')
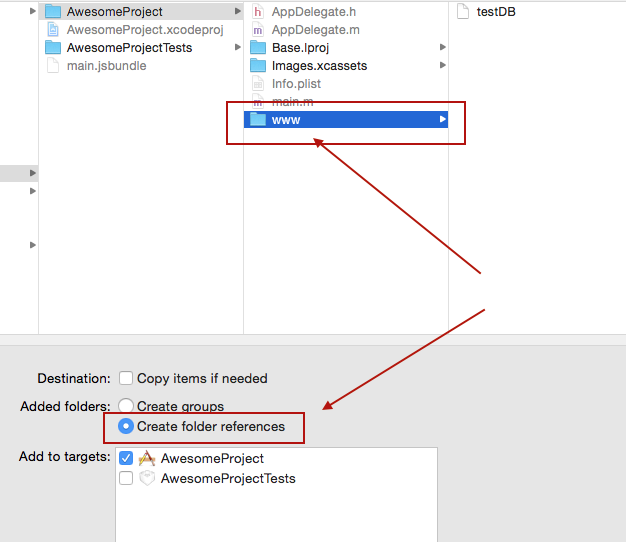
...Create a folder called 'www' (yes must be called precisely that else things won't work) in the project folder via Finder
Copy/paste your pre-populated database file into the 'www' folder. Give it the same name you are going to use in openDatabase call in your application
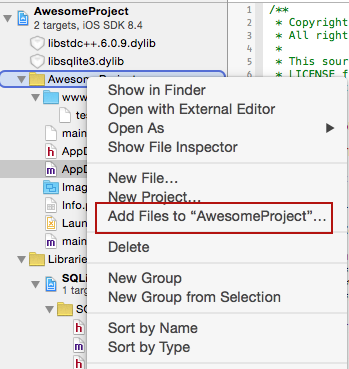
in XCode, right click on the main folder and select Add Files to 'your project name'
In the Add Files dialog, navigate to the 'www' directory you created in Step 1, select it, make sure you check the option to Create Folder Reference
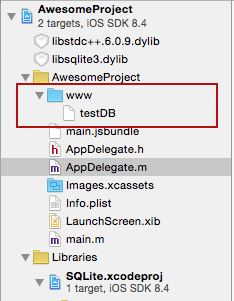
Ensure your project structure after previous steps are executed looks like this
Modify you openDatabase call in your application adding createFromLocation param. If you named your database file in step 2 'testDB' the openDatabase call should look like something like this:
...
SQLite.openDatabase({name : "testDB", createFromLocation : 1}, okCallback,errorCallback);
...Enjoy!
#Original Cordova SQLite Bindings from Chris Brody https://github.com/litehelpers/Cordova-sqlite-storage
The issues and limitations for the actual SQLite can be found on this site.
##Issues
- Android binds all numeric SQL input values to double. This is due to the underlying React Native limitation where only a Numeric type is available on the interface point making it ambiguous to distinguish intgeres from doubles. Once I figure out the proper way to do this I will update the codebase [(Issue #4141)] (facebook/react-native#4141).
- Automatic close for the database when main activity is destroyed is implemented in the pure Java Android version which is most likely to be obsoleted in the near future leaving native impl only.