THE AUTOMATED ELK STACK DEPLOYMENT
The files shown in this document and stored in this repository were used to configure the network depicted below:
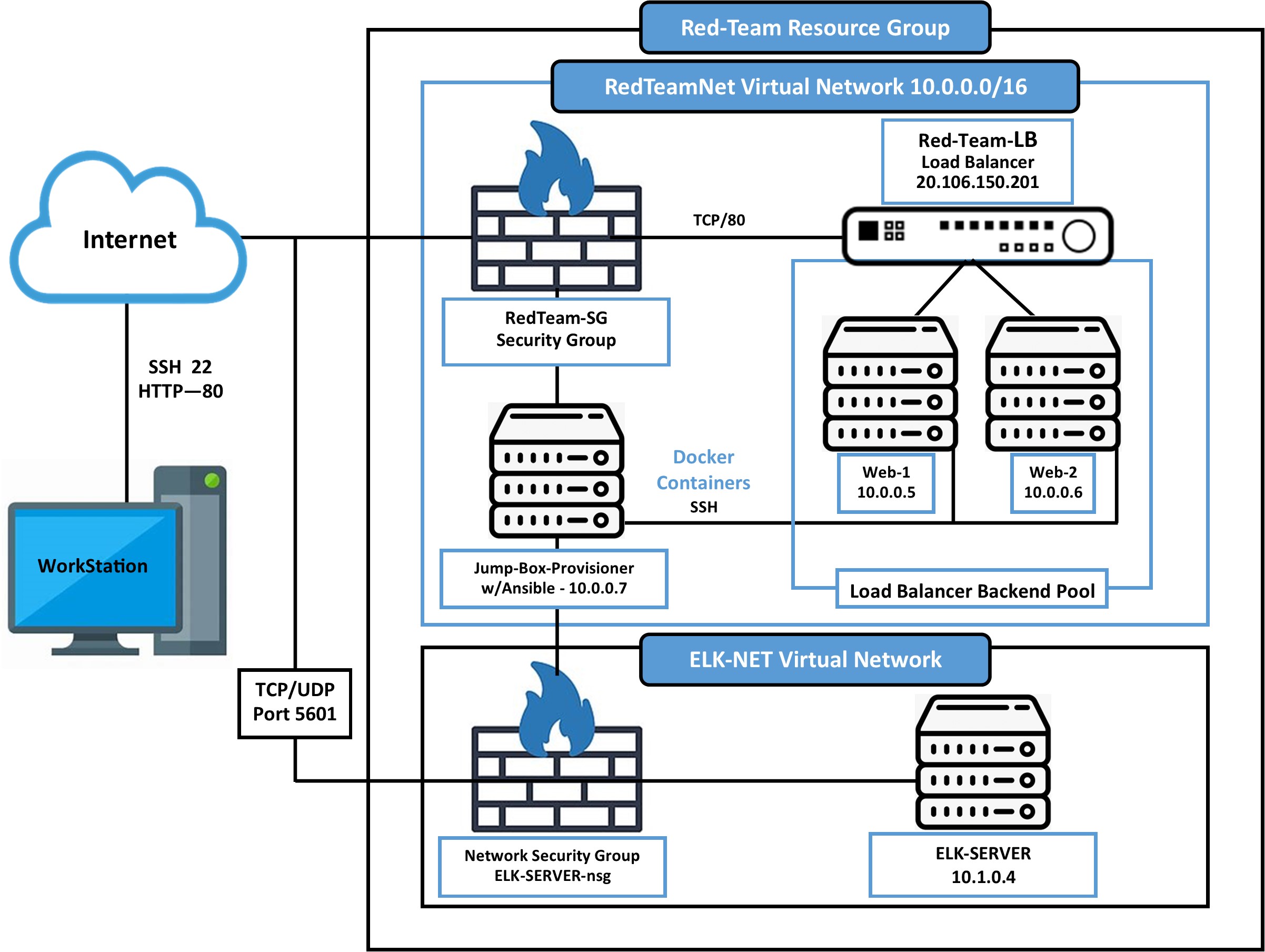 https://docs.google.com/document/d/1-xAqrazYwbKwtlJFryb5SoIfbFI6TOV2pJGhaSeH9F8/edit?usp=sharing
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1-xAqrazYwbKwtlJFryb5SoIfbFI6TOV2pJGhaSeH9F8/edit?usp=sharing
These files have been tested and used to generate a live ELK deployment on Azure. They can be used to either recreate the entire deployment pictured above or, alternatively, select portions of the playbook file can be used to install only certain pieces of it, such as Filebeats.
This document contains the following details:
- Description of the Topology
- Access Policies
- ELK Configuration
- Beats in Use
- Machines Being Monitored
- How to Use the Ansible Build
Description of the Topology
The main purpose of this network is to expose a load-balanced and monitored instance of DVWA, the D*mn Vulnerable Web Application.
Load balancing ensures that the application will be highly available, efficient and reliable, in addition to restricting access to the network. Also, with health probes, load balancers improve application “up time” by routing traffic to healthy nodes.
What aspect of security do load balancers protect? What is the advantage of a jump box?
The off-loading function of a load balancer defends an organization against distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. It does this by shifting attack traffic from the corporate server to a public cloud provider. (Source: https://avinetworks.com/what-is-load-balancing/). The load balancer, as the name implies, insures that the work to process incoming traffic is shared by all load balanced servers.
Integrating an ELK server allows users to easily monitor the 1) vulnerable VMs for changes to the file systems of the servers on the network, and also 2) the system metrics such as CPU usage, attempted SSH logins, sudo escalation failures, etc.
-
Filebeats watch for changes to the file system. Specifically, we use it to collect Apache logs. The Apache HTTP Server provides very comprehensive and flexible logging capabilities. Apache httpd is capable of writing error and access log files through a pipe to another process, rather than directly to a file. This dramatically increases the flexibility of logging, without adding code to the main server. (Source: https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/logs.html ) - Piped Logs.
-
Metricbeats record and monitor statistics from the running servers to help identify changes in system measurements. Data retrieved can include operating system metrics such as CPU or memory usage, or data related to services running on the server(s).
The configuration details of each machine are listed below.
| Name | Function | IP Address | Operating System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jump Box Provisioner | Gateway/Ansible | 10.0.0.7 | Linux |
| Web-1 | Web Server | 10.0.0.5 | Linux |
| Web-2 | Web Server | 10.0.0.6 | Linux |
| Elk-Server | Monitoring Server | 10.1.0.4 | Linux |
Access Policies
The machines on the internal network are not exposed to the public Internet.
Only the Jump-box machine can accept connections from the Internet. Access to this machine is only allowed from the following IP addresses: 68.203.13.109 (my local host public IP address, IPV4)
Machines within the network can only be accessed by each other.
I allowed the Jump-box to access my ELK VM. The IP address used: 10.0.0.7
A summary of the access policies in place can be found in the table below.
| Name | Publicly Accessible | Private IP Address |
|---|---|---|
| Jump Box Provisioner | Yes (20.120.82.127) | 10.0.0.7 |
| Web-1 | No | 10.0.0.5 |
| Web-2 | No | 10.0.0.6 |
| Elk-Server | No | 10.1.0.4 |
Elk Configuration
Ansible was used to automate configuration of the ELK machine. No configuration was performed manually, which is particularly advantageous because it avoids human error. Using automation allows for much greater scaling andr reduces administrative burden.
Another great advantage of automating the configurations for Ansible is that it allows an administrator to deploy multiple servers with a single YAML playbook with minimal changes.
The ELK playbook (elk.yml):
 https://drive.google.com/file/d/1MGSwMVfCJQA940oCfsTIqUULITDrNBmz/view?usp=sharing
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1MGSwMVfCJQA940oCfsTIqUULITDrNBmz/view?usp=sharing
This playbook implements the following tasks as indicated in the elk.yml file:
- Configure Elk VM with Docker
- Install docker.io
- Install pip3
- Note: pip is a package manager for Python. It is a tool that allows you to install and manage additional libraries and dependencies that are not distributed as part of the standard library. Package management is so important that pip has been included with the Python installer since versions 3.4 for Python 3 and 2.7.9 for Python 2, and it is used by many Python projects, which makes it an essential tool.
(Source: What Is Pip? A Guide for New Pythonistas – Real Python)
- Install Docker python module
- Download and launch a docker elk container
The following screenshot displays the result of running docker ps after successfully configuring the ELK instance.
 https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Z-SH9tVglsCW5zIS5EOxvdMPbYTpBdbg/view?usp=sharing
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Z-SH9tVglsCW5zIS5EOxvdMPbYTpBdbg/view?usp=sharing
Target Machines & Beats in Use
This ELK server is configured to monitor the following machines:
- Web-1 – 10.0.0.5
- Web-2 – 10.0.0.6
I only installed Filebeats on my machine. The other available for installation was Metricbeats.
-
Filebeats is a log message provider. Its principle of operation is to monitor and collect log messages from log files and send them to Elasticsearch or LogStash for indexing. Examples of what I would expect to see is information logged on SSH logins and sudo commands.
-
Metricbeats (not installed on my system) – collects metrics that developers can use with the Kibana dashboard to visualize the information received.
Using the Playbook
In order to use the playbook, you will need to have an Ansible control node already configured. Assuming you have such a control node provisioned (our control node is the Jump box) SSH into the Jump box and follow the steps below:
-
COPY the playbook file to /etc/ansible (cd /etc/ansible) The /etc/ansible directory contains the files: ansible.cfg, elk.yml, and hosts.
-
UPDATE the hosts file to include ip addresses for webservers (Web-1 & Web-2) as well as the ELK virtual machine.
-
RUN the playbook and navigate to the Kibana website dashboard to check that the installation worked as expected.
Recap:
-
Which file is the playbook? The playbook is a YAML file (extension .yml). For example, the elk.yml file would be copied into the /etc/ansible directory (you may create a “files” directory and place necessary files there).
-
Which file do you update to make Ansible run the playbook on a specific machine? Hosts
-
To run the playbook, cd to the /etc/ansible directory.
Then, run the appropriate command(s): ansible-playbook install_elk.yml, ansible-playbook install_filebeat.yml webservers, etc. -
Which URL do you navigate to to check that the ELK server is running? When the ELK machine is up and running, use the curl command or open a new browser and use the public ip address & port 5601 for the ELK machine (20.110.123.43).
http://[ **20.110.123.43**]:5601/app/kibana
Bonus**
- I used the nano command to edit and update the yaml files.

