Align introduces a better alternative to Auto Layout anchors.
- Semantic. Align APIs focus on your goals, not the math behind Auto Layout constraints.
- Powerful. Create multiple constraints with a single line of code.
- Type Safe. Makes it impossible to create invalid constraints, at compile time.
- Fluent. Concise and clear API that follows Swift API Design Guidelines.
- Simple. Stop worrying about
translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraintsand constraints activation.
To give you a taste of what the semantic APIs look like, here is an example:
view.anchors.edges.pin(insets: 20, alignment: .center)You can choose to add convenience extensions that you prefer to make it even more concise for select use cases, e.g.
view.pin(insets: 20).
The entire library fits in a single file with around 300 lines of code. You can simply drag-n-drop it into your app if you'd like. For more installation options, see Installation Guide.
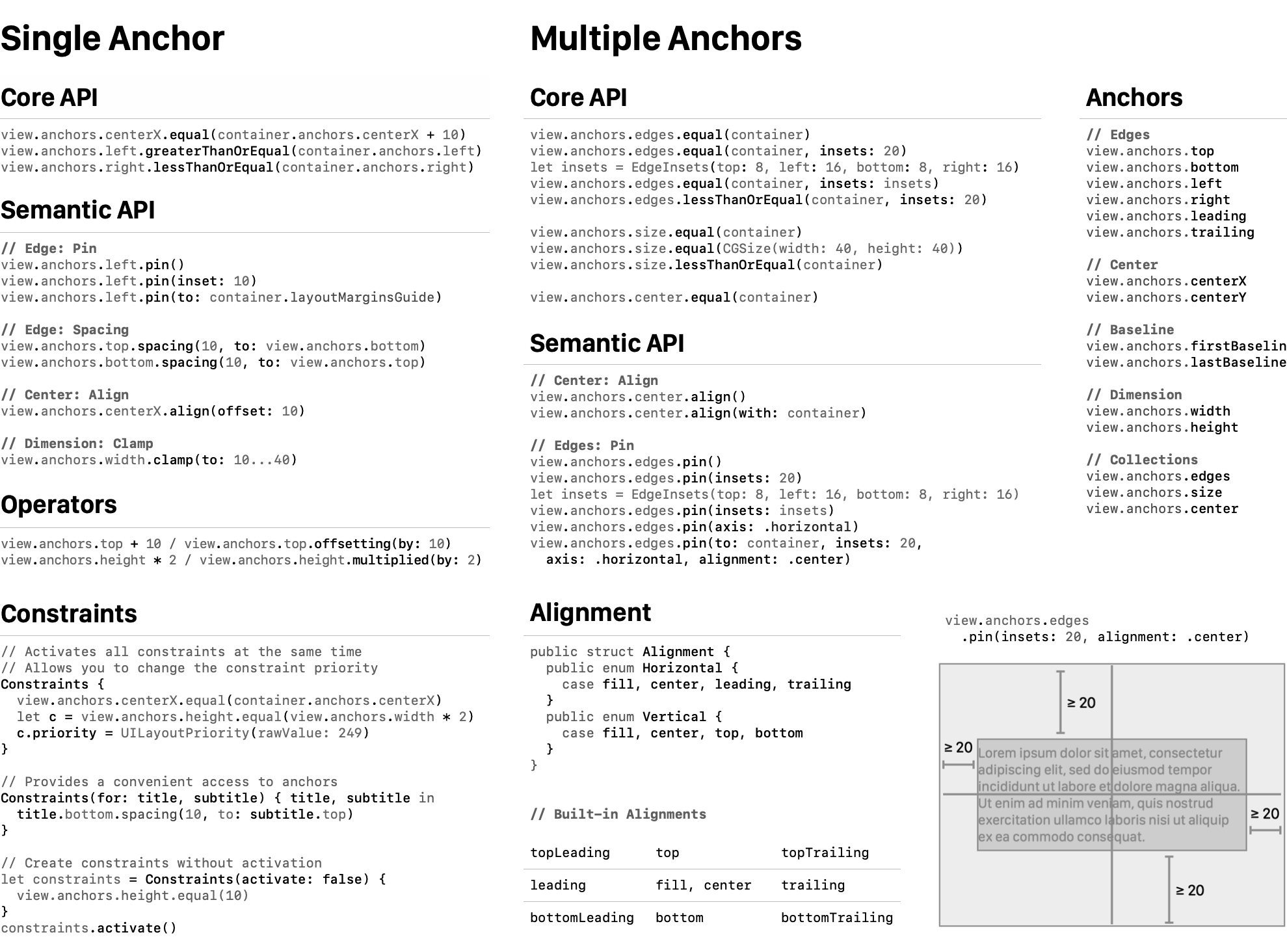
- Anchors ‣ Introduction · Core API · Semantic API
- Anchor Collections ‣ Edges · Center · Size
- Advanced · Requirements · Why Align
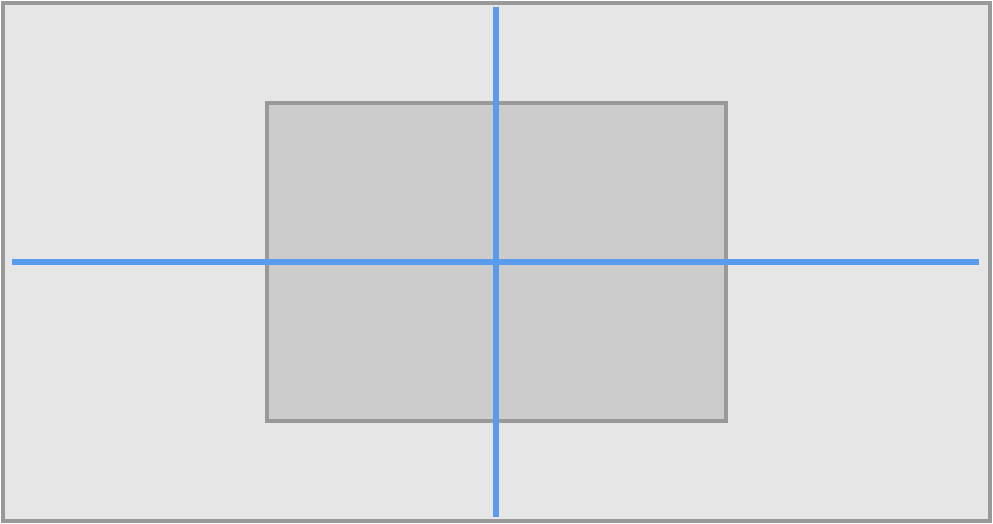
Anchors (Anchor<Type, Axis) represent layout attributes of a view including edges, dimensions, axis, and baselines. You use anchors to create constraints. The Align APIs fit in the following quadrant:
Core API allows you to create constraints by setting relations between one or more anchors, there APIs are similar to what NSLayoutAnchor provides. Semantic API is a high-level API that focus on your goals, such as pinning edges to the container, aligning the view, setting spacing between views, etc.
Both of these types of APIs are designed to be easily discoverable using Xcode code completions. There is also a cheat sheet available, as well as an illustrated guide located in this README.
// Align two views along one of the edges
a.anchors.leading.equal(b.anchors.leading)
// Other options are available:
// a.anchors.leading.greaterThanOrEqual(b.anchors.leading)
// a.anchors.leading.greaterThanOrEqual(b.anchors.leading, constant: 10)
// Set height to the given value (CGFloat)
a.anchors.height.equal(30)Align automatically sets translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints to false for every view that you manipulate using it, so you no longer have to worry about it.
Align also automatically activates the created constraints. Using (NSLayoutConstraint.active(_:) is typically slightly more efficient than activating each constraint individually. To take advantage of this method, wrap your code into Constrains initializer.
Constraints {
// Create constraints in this closure
}Align has full test coverage. If you'd like to learn about which constraints (
NSLayoutConstraint) Align creates each time you call one of its methods, test cases are a great place to start.
Align also allows you to offset and multiply anchors. This is a lightweight operation with no allocations involved.
// Offset one of the anchors, creating a "virtual" anchor
b.anchors.leading.equal(a.anchors.trailing + 20)
// Set aspect ratio for a view
b.anchors.height.equal(a.anchors.width * 2)// Set spacing between two views
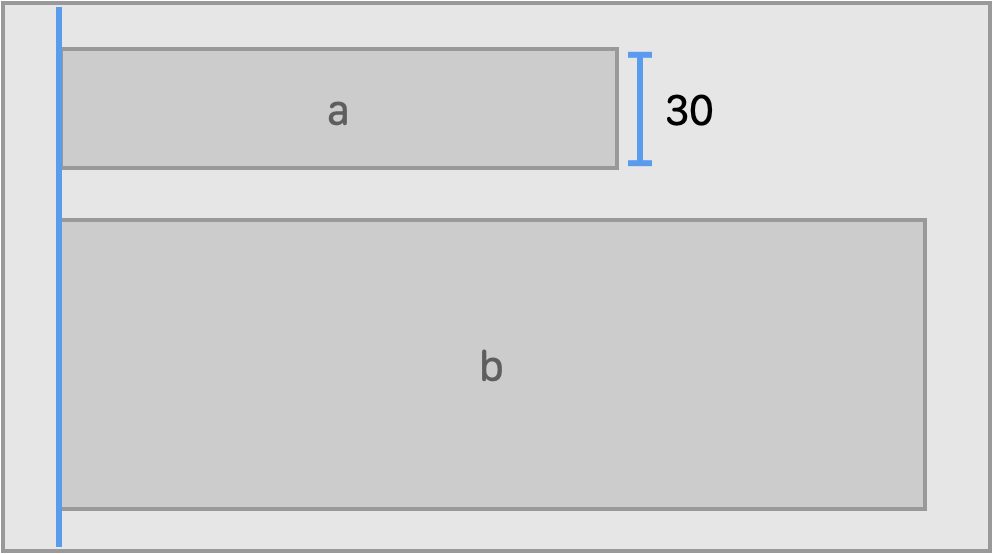
a.anchors.bottom.spacing(20, to: b.anchors.top)
// Pin an edge to the superview
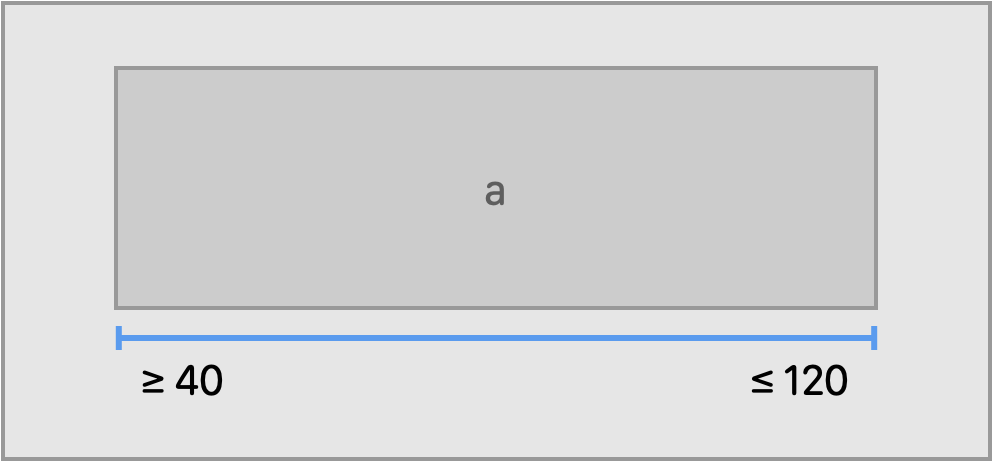
a.anchors.trailing.pin(inset: 20)Clamps the dimension of a view to the given limiting range.
a.anchors.width.clamp(to: 40...100)With Align, you can manipulate multiple edges at the same time, creating more than one constraint at a time.
pin() is probably the most powerful and flexible API in Align.
view.anchors.edges.pin(insets: 20)
// Same as the following:
view.anchors.edges.pin(
to: view.superview!
insets: EdgeInsets(top: 20, left: 20, bottom: 20, trailing: 20),
alignment: .fill
)By default, pin() method pin the edges to the superview of the current view. However, you can select any target view or layout guide:
// Pin to superview
view.anchors.edges.pin()
// Pin to layout margins guide
view.anchors.edges.pin(to: container.layoutMarginsGuide)
// Pin to safe area
view.anchors.edges.pin(to: container.safeAreaLayoutGuide)Align also provides a convenient way to access anchors of the layout guide:
view.anchors.safeArea.top.
By default, pin() users .fill alignment. There are variety of other alignments available (81 if you combine all possible options).
view.anchors.edges.pin(insets: 20, alignment: .center)You can create constraint along the given axis.
view.anchors.edges.pin(insets: 20, axis: .horizontal, alignment: .center)Or pin the view to to a corner.
view.anchors.edges.pin(insets: 20, alignment: .topLeading)You can create custom alignments (see Alignment type) by providing a vertical and horizontal component.
anchors.edges.pin(insets: 20, alignment: Alignment(vertical: .center, horizontal: .leading))a.anchors.center.align()a.anchors.size.equal(CGSize(width: 120, height: 40))
greaterThanEqualandlessThanOrEqualoptions are also available
a.anchors.size.equal(b)By default, Align automatically activates created constraints. Using Constraints API, constraints are activated all of the same time when you exit from the closure. It gives you a chance to change the priority of the constraints.
Constraints(for: title, subtitle) { title, subtitle in
// Align one anchor with another
subtitle.top.spacing(10, to: title.bottom + 10)
// Manipulate dimensions
title.width.equal(100)
// Change a priority of constraints inside a group:
subtitle.bottom.pin().priority = UILayoutPriority(999)
}Constraints also give you easy access to Align anchors (notice, there is no .anchors call in the example). And if you want to not activate the constraints, there is an option for that:
Constraints(activate: false) {
// Create your constraints here
}| Align | Swift | Xcode | Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Align 2.0 | Swift 5.1 | Xcode 11.0 | iOS 11.0 / tvOS 11.0 / macOS 10.13 |
| Align 1.1-1.2 | Swift 4.2 – 5.0 | Xcode 10.1 – 10.2 | iOS 10.0 / tvOS 10.0 |
| Align 1.0 | Swift 4.0 – 4.2 | Xcode 9.2 – 10.1 | iOS 9.0 / tvOS 9.0 |
Align strives for clarity and simplicity by following Swift API Design Guidelines. Although most of the APIs are compact, it is a non-goal to enable the most concise syntax possible.
Align is for someone who:
- Prefers fluent API that follows Swift API Design Guidelines
- Doesn't want to depend on big, complex libraries
- Prefers to have as little extensions for native classes as possible,
Alignonly adds one property - Doesn't overuse operator overloads, prefers fast compile times
- Likes NSLayoutAnchor but wishes it had simpler, more fluent API which didn't require manually activating constraints