By Transistor Software, creators of Flutter Background Geolocation
Background Fetch is a very simple plugin which will awaken an app in the background about every 15 minutes, providing a short period of background running-time. This plugin will execute your provided callbackFn whenever a background-fetch event occurs.
🆕 Background Fetch now provides a scheduleTask method for scheduling arbitrary "one-shot" or periodic tasks.
- There is no way to increase the rate which a fetch-event occurs and this plugin sets the rate to the most frequent possible — you will never receive an event faster than 15 minutes. The operating-system will automatically throttle the rate the background-fetch events occur based upon usage patterns. Eg: if user hasn't turned on their phone for a long period of time, fetch events will occur less frequently.
scheduleTaskseems only to fire when the device is plugged into power.
- The Android plugin provides a Headless implementation allowing you to continue handling events even after app-termination.
📂 pubspec.yaml:
dependencies:
background_fetch: '^0.5.1'dependencies:
background_fetch:
git:
url: https://github.com/transistorsoft/flutter_background_fetchimport 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
import 'package:background_fetch/background_fetch.dart';
/// This "Headless Task" is run when app is terminated.
void backgroundFetchHeadlessTask(String taskId) async {
print('[BackgroundFetch] Headless event received.');
BackgroundFetch.finish(taskId);
}
void main() {
// Enable integration testing with the Flutter Driver extension.
// See https://flutter.io/testing/ for more info.
runApp(new MyApp());
// Register to receive BackgroundFetch events after app is terminated.
// Requires {stopOnTerminate: false, enableHeadless: true}
BackgroundFetch.registerHeadlessTask(backgroundFetchHeadlessTask);
}
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_MyAppState createState() => new _MyAppState();
}
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
bool _enabled = true;
int _status = 0;
List<DateTime> _events = [];
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
initPlatformState();
}
// Platform messages are asynchronous, so we initialize in an async method.
Future<void> initPlatformState() async {
// Configure BackgroundFetch.
BackgroundFetch.configure(BackgroundFetchConfig(
minimumFetchInterval: 15,
stopOnTerminate: false,
enableHeadless: false,
requiresBatteryNotLow: false,
requiresCharging: false,
requiresStorageNotLow: false,
requiresDeviceIdle: false,
requiredNetworkType: NetworkType.NONE
), (String taskId) async {
// This is the fetch-event callback.
print("[BackgroundFetch] Event received $taskId");
setState(() {
_events.insert(0, new DateTime.now());
});
// IMPORTANT: You must signal completion of your task or the OS can punish your app
// for taking too long in the background.
BackgroundFetch.finish(taskId);
}).then((int status) {
print('[BackgroundFetch] configure success: $status');
setState(() {
_status = status;
});
}).catchError((e) {
print('[BackgroundFetch] configure ERROR: $e');
setState(() {
_status = e;
});
});
// Optionally query the current BackgroundFetch status.
int status = await BackgroundFetch.status;
setState(() {
_status = status;
});
// If the widget was removed from the tree while the asynchronous platform
// message was in flight, we want to discard the reply rather than calling
// setState to update our non-existent appearance.
if (!mounted) return;
}
void _onClickEnable(enabled) {
setState(() {
_enabled = enabled;
});
if (enabled) {
BackgroundFetch.start().then((int status) {
print('[BackgroundFetch] start success: $status');
}).catchError((e) {
print('[BackgroundFetch] start FAILURE: $e');
});
} else {
BackgroundFetch.stop().then((int status) {
print('[BackgroundFetch] stop success: $status');
});
}
}
void _onClickStatus() async {
int status = await BackgroundFetch.status;
print('[BackgroundFetch] status: $status');
setState(() {
_status = status;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new MaterialApp(
home: new Scaffold(
appBar: new AppBar(
title: const Text('BackgroundFetch Example', style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black)),
backgroundColor: Colors.amberAccent,
brightness: Brightness.light,
actions: <Widget>[
Switch(value: _enabled, onChanged: _onClickEnable),
]
),
body: Container(
color: Colors.black,
child: new ListView.builder(
itemCount: _events.length,
itemBuilder: (BuildContext context, int index) {
DateTime timestamp = _events[index];
return InputDecorator(
decoration: InputDecoration(
contentPadding: EdgeInsets.only(left: 10.0, top: 10.0, bottom: 0.0),
labelStyle: TextStyle(color: Colors.amberAccent, fontSize: 20.0),
labelText: "[background fetch event]"
),
child: new Text(timestamp.toString(), style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 16.0))
);
}
),
),
bottomNavigationBar: BottomAppBar(
child: Row(
children: <Widget>[
RaisedButton(onPressed: _onClickStatus, child: Text('Status')),
Container(child: Text("$_status"), margin: EdgeInsets.only(left: 20.0))
]
)
),
),
);
}
}In addition to the default background-fetch task defined by BackgroundFetch.configure, you may also execute your own arbitrary "oneshot" or periodic tasks (iOS requires additional Setup Instructions). However, all events will be fired into the Callback provivded to BackgroundFetch#configure:
// Step 1: Configure BackgroundFetch as usual.
BackgroundFetch.configure(BackgroundFetchConfig(
minimumFetchInterval: 15
), (String taskId) async {
// This is the fetch-event callback.
print("[BackgroundFetch] taskId: $taskId");
// Use a switch statement to route task-handling.
switch (taskId) {
case 'com.transistorsoft.customtask':
print("Received custom task");
break;
default:
print("Default fetch task");
}
// Finish, providing received taskId.
BackgroundFetch.finish(taskId);
});
// Step 2: Schedule a custom "oneshot" task "com.transistorsoft.customtask" to execute 5000ms from now.
BackgroundFetch.scheduleTask(TaskConfig(
taskId: "com.transistorsoft.customtask",
delay: 5000 // <-- milliseconds
));⚠️ At the time of writing, the new task simulator does not yet work in Simulator; Only real devices.- See Apple docs Starting and Terminating Tasks During Development
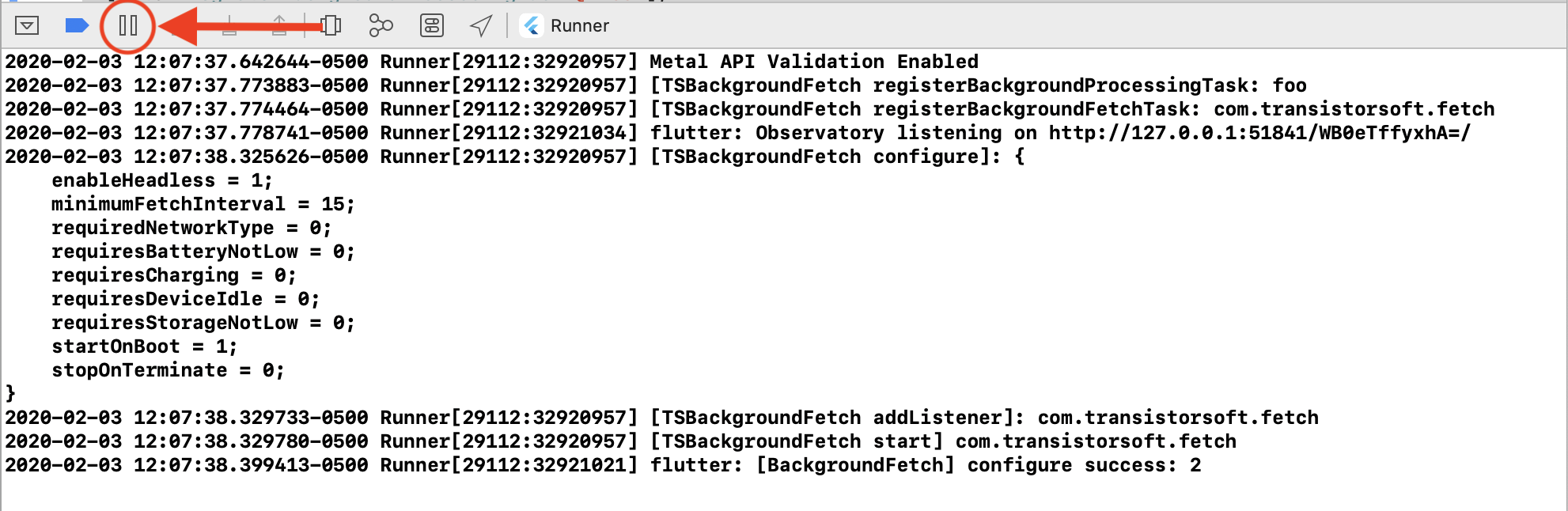
- After running your app in XCode, Click the
[||]button to initiate a Breakpoint. - In the console
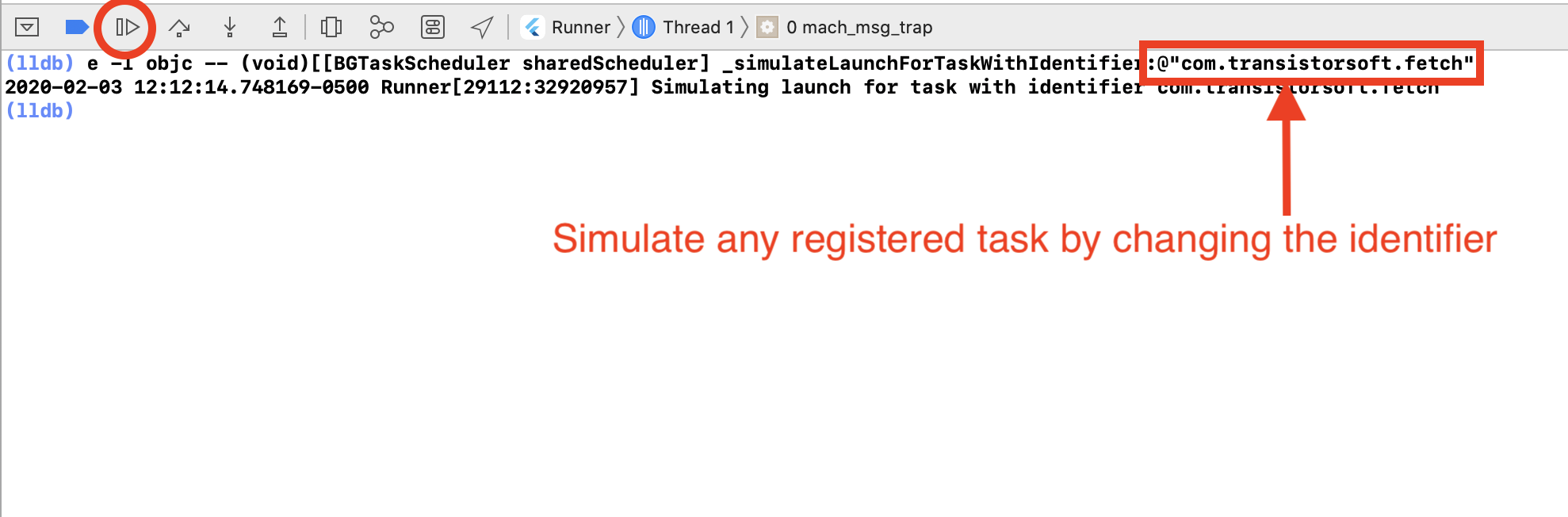
(lldb), paste the following command (Note: use cursor up/down keys to cycle through previously run commands):
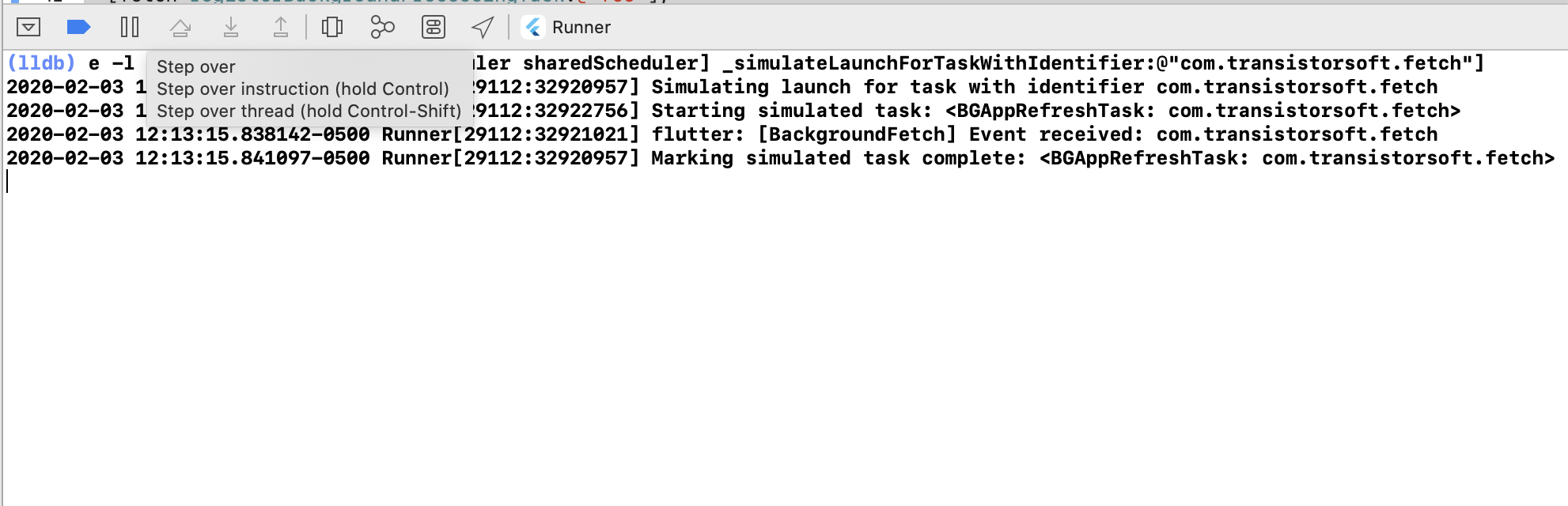
e -l objc -- (void)[[BGTaskScheduler sharedScheduler] _simulateLaunchForTaskWithIdentifier:@"com.transistorsoft.fetch"]- Click the
[ > ]button to continue. The task will execute and the Callback function provided toBackgroundFetch.configurewill receive the event.
- Simulate background fetch events in XCode using
Debug->Simulate Background Fetch - iOS can take some hours or even days to start a consistently scheduling background-fetch events since iOS schedules fetch events based upon the user's patterns of activity. If Simulate Background Fetch works, your can be sure that everything is working fine. You just need to wait.
- Observe plugin logs in
$ adb logcat:
$ adb logcat *:S flutter:V, TSBackgroundFetch:V- Simulate a background-fetch event on a device (insert <your.application.id>) (only works for sdk
21+:
$ adb shell cmd jobscheduler run -f <your.application.id> 999- For devices with sdk
<21, simulate a "Headless" event with (insert <your.application.id>)
$ adb shell am broadcast -a <your.application.id>.event.BACKGROUND_FETCH
This repo contains an /example folder. Clone this repo and open the /example folder in Android Studio.
Implements performFetchWithCompletionHandler, firing a custom event subscribed-to in cordova plugin.
Android implements background fetch using two different mechanisms, depending on the Android SDK version. Where the SDK version is >= LOLLIPOP, the new JobScheduler API is used. Otherwise, the old AlarmManager will be used.
Unlike iOS, the Android implementation can continue to operate after application terminate (stopOnTerminate: false) or device reboot (startOnBoot: true).
The MIT License
Copyright (c) 2018 Chris Scott, Transistor Software [email protected] https://www.transistorsoft.com
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.