Database is collectation of inter-related of inter-related data, from which we can easily manipulate data.
In a database have multiple entity & in a entity have multiple attributes.
SQL - Structured query language is used to communicate with a database. According to ANSI (American National Standards Institute), it is the standard language for relational database management systems.
CREATE DATABASE databasename;
CREATE DATABASE db_name
CHARACTER SET utf8
COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci;
ALTER DATABASE db_name
[DEFAULT] CHARACTER SET charset_name]
[DEFAULT] COLLATE collation_name]
DROP DATABASE database_name;
-- Single line Comment define with [--]
/*
multi-line comment with /*...*/
*/
Syntax:
Create table table_name(
colmn_name datatype constrains
);
Example:
Create table users(
id int not null auto_increment,
name varchar(100),
email varchar(50),
password varchar(100),
PRIMARY KEY(id)
);
DROP TABLE table_name
The ALTER TABLE statement is used to add, delete, or modify columns in an existing table.
And also used to add and drop various constraints on an existing table.
ALTER TABLE authors
RENAME author
ALTER TABLE table_name
change existing_column new_column_name datatype;
ALTER TABLE author
change mail email varchar(20);
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD column_name datatype;
ALTER TABLE users
ADD password varchar(100);
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP column_name;
ALTER TABLE users
DROP password;
SQL constraints (বাদ্ধ্যবাধকতা) are used to specify rules for data in a table.
Available constraints in SQL:
- NOT NULL - Ensures that a column cannot have a NULL value
- NULL - a column can have a NULL value
- UNIQUE - Ensures that all values in a column are different
- DEFAULT
- PRIMARY KEY
- FOREIGN KEY
- CHECK
- CREATE INDEX
The DEFAULT constraint is used to set a default value for a column.
column_name datatype DEFAULT value;
The PRIMARY KEY constraint uniquely identifies each record in a table.
Primary keys must contain UNIQUE values, and cannot contain NULL values.
CREATE TABLE Users (
id int NOT NULL auto_increment,
age int,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
A FOREIGN KEY is a field (or collection of fields) in one table, that refers to the PRIMARY KEY in another table.
CREATE TABLE Users (
id int NOT NULL auto_increment,
age int,
role_id int,
PRIMARY KEY (id),
FOREGIN KEY (role_id) REFERENCES roles(role_id)
);
Add Foregin key on existing column of a table :
ALTER TABLE Orders
ADD FOREIGN KEY (PersonID)
REFERENCES Persons(PersonID);
Drop Foregin key form a table :
ALTER TABLE Orders
DROP FOREIGN KEY PersonID;
The CHECK constraint is used to limit the value range that can be placed in a column.
CREATE TABLE Users (
ID int NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int,
CHECK (Age>=18)
);
ALTER TABLE users
ADD CHECK (Age>=18);
ALTER TABLE Persons
DROP CHECK CHK_PersonAge;
The CREATE INDEX statement is used to create indexes in tables.
Indexes are used to retrieve data from the database more quickly than otherwise. The users cannot see the indexes, they are just used to speed up searches/queries.
CREATE INDEX index_name
ON table_name (col1,col2,...);
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP INDEX index_name
SELECT QUERY is used to fetch the data from database.
It is the most frequently used SQL command and has the following general syntax:
SELECT
[DISTINCT|ALL ]
{ * | [fieldExpression [AS newName]}
FROM tableName
[alias]
[WHERE condition]
[GROUP BY fieldName(s)]
[HAVING condition]
ORDER BY fieldName(s)
Here,
SELECT is the SQL keyword that lets the database know that you want to retrieve data.
[DISTINCT | ALL] are optional keywords that can be used to fine tune the results returned from the SQL SELECT statement. If nothing is specified then ALL is assumed as the default.
{*| [fieldExpression [AS newName]} at least one part must be specified, "*" selected all the fields from the specified table name, fieldExpression performs some computations on the specified fields such as adding numbers or putting together two string fields into one.
FROM tableName is mandatory and must contain at least one table, multiple tables must be separated using commas or joined using the JOIN keyword.
WHERE condition is optional, it can be used to specify criteria in the result set returned from the query.
GROUP BY is used to put together records that have the same field values.
HAVING condition is used to specify criteria when working using the GROUP BY keyword.
ORDER BY is used to specify the sort order of the result set.
SELECT * FROM users;
Select specific column data :
-------------------
SELECT name,email FROM users;
Using `AS` Keyword, you can set a customize name on any column when select a data :
-------------------
SELECT name AS user_name, email AS user_mail FROM users;
Concat multiple column data :
-------------------
SELECT CONCAT(column1,column2,..) AS new_column FROM table;
Select distinct : (it returns only different values)
-------------------
SELECT DISTINCT name FROM users;
WHERE Clause in MySQL is a keyword used to specify the exact criteria of data or rows that will be affected by the specified SQL statement. The WHERE clause can be used with SQL statements like INSERT, UPDATE, SELECT, and DELETE to filter records and perform various operations on the data.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM tableName WHERE condition;
SELECT * FROM users WHERE age>30;
NB: Where clause combined with logical operator[>,<,<>,AND, OR, NOT] & some keyword to implement conditions better way.
where condition1, condition2 both are ture
SELECT * FROM `users` WHERE `age` >= 18 AND `sex` = 'male';
where condition1, condition2 one or both will be true
SELECT * FROM `users` WHERE `age` >= 18 OR `sex` = 'male';
WHERE INreturns values that match values in a list.- This list is hardcoded or generated by a subquery.
- WHERE IN is shorthand for multiple OR conditions.
example :
SELECT * FROM film WHERE length IN(50, 55)
sub-query:
SELECT *
FROM language
WHERE language_id IN
(SELECT language_id FROM film )
*NB: if you want to select items that don't exist on the array/list, then you have to use NOT IN alter of IN
'INSERT INTO 'is used to store data in the tables.
Basic Syntax:
INSERT INTO tableName (col1, col2, col3, ...) VALUES (data1, data2, data3, ...);
Example :
INSERT INTO members (full_names,gender,physical_address,contact_number)
VALUES ('Sheldon Cooper','Male','Woodcrest', '0976736763');
NB: Changing the order of the columns has no effect on the INSERT query in MySQL as long as the correct values have been mapped to the correct columns.
The INSERT command can also be used to insert data into a table from another table. The basic syntax is as shown below.
INSERT INTO table_1 SELECT * FROM table_2;
example:
INSERT INTO categories_archive
SELECT * FROM categories;
speacific :
INSERT INTO categories_archive(category_id,category_name,remarks)
SELECT category_id,category_name,remarks FROM categories;
Delete command is used to delete rows that are no longer required from the database tables
Syntax :
DELETE FROM table_name [WHERE condition];
Example :
DELETE FROM users WHERE user_id = 1;
The UPDATE command can be used to update a single field or multiple fields at the same time. It can also be used to update a MySQL table with values from another table.
syntax:
UPDATE tablename
SET col1 = val1, col2 = val2,...
WHERE condition;
Example :
UPDATE books
SET name = 'Signature Mind', author_id = 1
WHERE id = 2;
ORDER BY clause is used to sort the data in ascending or descending order, based on one or more columns. Some databases sort the query results in an ascending order by default.
Syntax :
SELECT statement...
[WHERE condition | GROUP BY field_name(s) HAVING condition]
ORDER BY field_name(s) [ASC | DESC];
- Select is the regular select query " | " represents alternatives
- [ Where" condition | Group By
field_name(s)Having condition" is the optional condition used to filter the query result sets. ORDER BYperforms the query result set sorting[ASC | DESC]is the keyword used to sort result sets in either ascending or descending order. NoteASCis used as the default.
SELECT * FROM flim
ORDER BY country_id;
SELECT * FROM flim
ORDER BY country_id, release_year;
SELECT * FROM flim
ORDER BY country_id DESC;
SELECT * FROM flim
ORDER BY country_id ASC, release_year DESC;
*ASC use for ascending order
The limit keyword is used to limit the number of rows returned in a query result.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM tablename
...
LIMIT numberOfRows;
Example:
SELECT * FROM flim
WHERE language = 'en'
ORDER BY country_id DESC
LIMIT 5;
If you want the query to return entries starting from a particular line, you can use OFFSET clause to tell it where it should start. And the practrial example will be pagination.
Syntax :
SELECT * FROM tableName ...
LIMIT (n)
OFFSET (n)number
SELECT * FROM movie
WHERE category="action"
LIMIT 25
OFFEST 30;
Limit with offset :
SELECT * FROM tableName ...
LIMIT numberOfOffest, numberOfLimit;
SELECT * FROM movie
WHERE language = "en"
LIMIT 30, 25;
The GROUP BY clause is a SQL command that is used to group rows that have the same values. The GROUP BY clause is used in the SELECT statement. Optionally it is used in conjunction with aggregate functions to produce summary reports from the database.
That's what it does, summarizing data from the database.
The queries that contain the GROUP BY clause are called grouped queries and only return a single row for every grouped item.
SELECT [*|col1,col2 ...]
FROM tableName
GROUP BY columnName [|,col_N];
Example :
SELECT * FROM flim
WHERE language_id=1
GROUP BY release_year, rental_rate
With helping a aggregate functions we can get / generate report by some data group. Suppose we want total number of males and females in our database. We can use the following script shown below to do that.
SELECT gender,COUNT(membership_number) FROM members GROUP BY gender;
SELECT avg(length) as AvgLength, release_year FROM film
WHERE language_id=1
GROUP BY release_year
It's not always that we will want to perform groupings on all the data in a given table. There will be times when we will want to restrict our results to a certain given criteria. In such cases , we can use the HAVING clause
Suppose we want to know all the release years for movie category id 8.
SELECT * FROM film GROUP BY category_id,year_released HAVING category_id = 8;
MySQL Wildcards are characters that help search data matching complex criteria. Wildcards are used in conjunction with the LIKE comparison operator or with the NOT LIKE comparison operator.
Let's see some example:
Select employe details name starting with A :
SELECT * FROM employe WHERE name LIKE 'A%';
SELECT employe details name ending with Z :
SELECT * FROM employe WHERE name LIKE '%Z';
SELECT employe name contains EE;
SELECT * FROM employe WHERE name LIKE '%EE%';
Employe name contains 'a' in second place:
SELECT * FROM employe WHERE name LIKE '_a%'
Whose name contains 'a' in second place and name should be contain total five char.
SELECT * FROM employe WHERE name LIKE '_a___'
| Symble | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| % | Represents zero or more characters | bl% finds bl, black, blue, and blob |
| _ | {underscore} Represents a single character | h_t finds hot, hat, and hit |
| [] | Represents any single character within the brackets | h[oa]t finds hot and hat, but not hit |
| ^ | Represents any character not in the brackets | h[^oa]t finds hit, but not hot and hat |
| - | {dash} Represents a range of characters | c[a-b]t finds cat and cbt |
Regular Expressions help search data matching complex criteria. We looked at wildcards in the previous tutorial. compared to wildcards, regular expressions allow us to search data matching even more complex criterion.
Syntax :
SELECT statements ...
WHERE fieldName
REGEXP 'your pattern goes here';
Example :
SELECT * FROM movies WHERE title REGEXP '^[^abcd]';
Know more about regex :
Comming Soon
Aggregate Functions are all about
- Performing calculations on multiple rows
- Of a single column of a table
- And returning a single value. The ISO standard defines five (5) aggregate functions namely;
- COUNT
- SUM
- AVG
- MIN
- MAX
From a business perspective, different organization levels have different information requirements. Top levels managers are usually interested in knowing whole figures and not necessary the individual details.
The COUNT function returns the total number of values in the specified field. It works on both numeric and non-numeric data types. All aggregate functions by default exclude nulls values before working on the data.
SELECT COUNT(movie_id) FROM movierentals WHERE movie_id = 2;
The DISTINCT keyword that allows us to omit duplicates from our results. This is achieved by grouping similar values together .
SELECT DISTINCT movie_id FROM movierentals;
The MIN function returns the smallest value in the specified table field.
SELECT MIN(year_released) FROM movies;
Just as the name suggests, the MAX function is the opposite of the MIN function. It returns the largest value from the specified table field.
SELECT MAX(`year_released`) FROM `movies`;
Suppose we want a report that gives total amount of payments made so far. We can use the SUM function which returns the sum of all the values in the specified column. SUM works on numeric fields only. Null values are excluded from the result returned.
SELECT SUM(`amount_paid`) FROM `payments`;
MySQL AVG function returns the average of the values in a specified column. Just like the SUM function, it works only on numeric data types.
SELECT AVG(`amount_paid`) FROM `payments`;
A sub-query is a select query that is contained inside another query. The innner select query is usually used to determine the result of the outer select query.
SELECT category_name
FROM categories
WHERE category_id =( SELECT MIN(category_id) from movies);
When compare with Joins , sub-queries are simple to use and easy to read. They are not as complicated as Joins
Hence there are frequently used by SQL beginners.
But sub-queries have performance issues. Using a join instead of a sub-query can at times give you upto 500 times performance boost.
Given a choice, it is recommended to use a JOIN over a sub query.
Sub-Queries should only be used as a fallback solution when you cannot use a JOIN operation to achieve the above
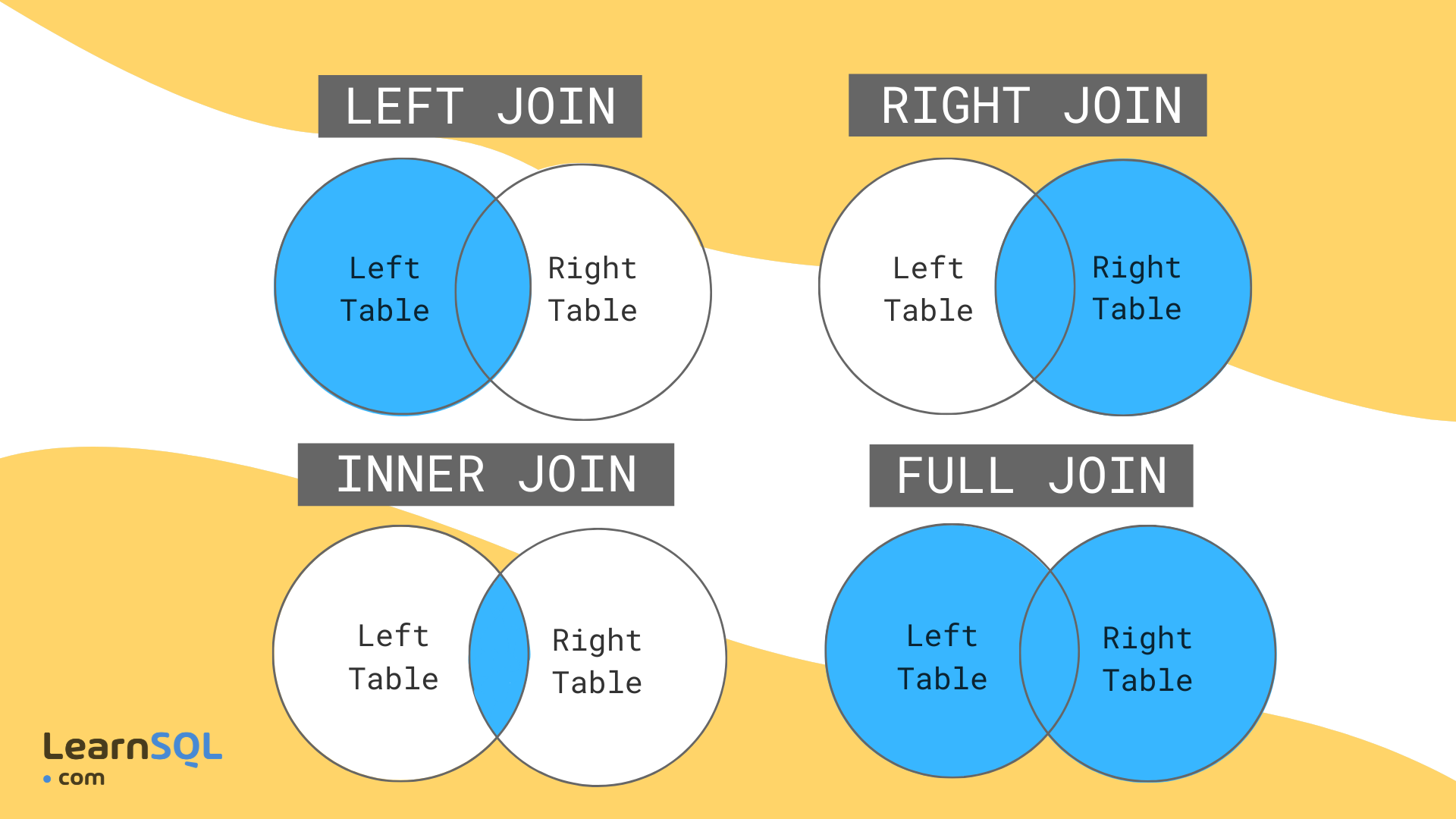
Joins help retrieving data from two or more database tables.
The tables are mutually related using primary and foreign keys.
The following are the types of JOIN that can be used in MySQL:
- (INNER) JOIN - returns records that have matching values in both tables
- LEFT JOIN (OUTER) - returns all records from the left table, and the matched records from the right table
- RIGHT JOIN (OUTER) - returns all records from the right table, and the matched records from the left table
to be more clear on the topic let's see the picture below:
Systax of join :
SELECT column/s
FROM tableOne
[INNER/LEFT/RIGHT] JOIN tableTwo
ON tableOne.columnName = tableTwo.columnName;
...statements;
- W3Schools
- Guru99
- DBMS By Gate Smashers --tutorial_hindi
- geekforgeeks
- Sololearn