Topics:
- Queues
- Stacks
- Doubly Linked Lists
- Singly Linked Lists
- Binary Search Trees
- Tree Traversal
- Sortings
- Searchings
- Dynamic Programming
- Heap
- Graph
- Should have the methods:
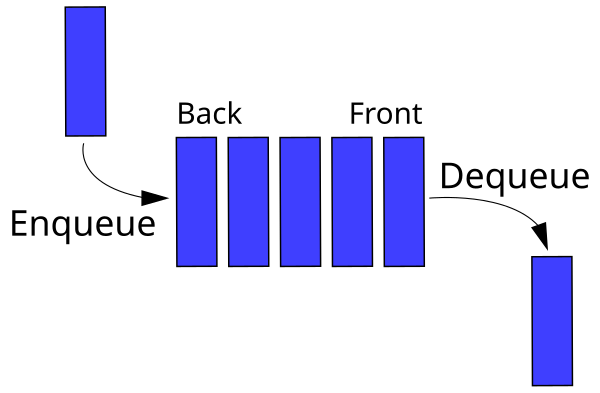
enqueue,dequeue, andlen.enqueueshould add an item to the back of the queue.dequeueshould remove and return an item from the front of the queue.lenreturns the number of items in the queue.
- The
ListNodeclass, which represents a single node in the doubly-linked list, has already been implemented for you. Inspect this code and try to understand what it is doing to the best of your ability. - The
DoublyLinkedListclass itself should have the methods:add_to_head,add_to_tail,remove_from_head,remove_from_tail,move_to_front,move_to_end,delete, andget_max.add_to_headreplaces the head of the list with a new value that is passed in.add_to_tailreplaces the tail of the list with a new value that is passed in.remove_from_headremoves the head node and returns the value stored in it.remove_from_tailremoves the tail node and returns the value stored in it.move_to_fronttakes a reference to a node in the list and moves it to the front of the list, shifting all other list nodes down.move_to_endtakes a reference to a node in the list and moves it to the end of the list, shifting all other list nodes up.deletetakes a reference to a node in the list and removes it from the list. The deleted node'spreviousandnextpointers should point to each afterwards.get_maxreturns the maximum value in the list.
- The
headproperty is a reference to the first node and thetailproperty is a reference to the last node.
- Should have the methods
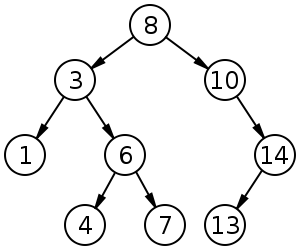
insert,contains,get_max.insertadds the input value to the binary search tree, adhering to the rules of the ordering of elements in a binary search tree.containssearches the binary search tree for the input value, returning a boolean indicating whether the value exists in the tree or not.get_maxreturns the maximum value in the binary search tree.for_eachperforms a traversal of every node in the tree, executing the passed-in callback function on each tree node value. There is a myriad of ways to perform tree traversal; in this case any of them should work.
- Should have the methods
insert,delete,get_max,_bubble_up, and_sift_down.insertadds the input value into the heap; this method should ensure that the inserted value is in the correct spot in the heapdeleteremoves and returns the 'topmost' value from the heap; this method needs to ensure that the heap property is maintained after the topmost element has been removed.get_maxreturns the maximum value in the heap in constant time.get_sizereturns the number of elements stored in the heap._bubble_upmoves the element at the specified index "up" the heap by swapping it with its parent if the parent's value is less than the value at the specified index._sift_downgrabs the indices of this element's children and determines which child has a larger value. If the larger child's value is larger than the parent's value, the child element is swapped with the parent.