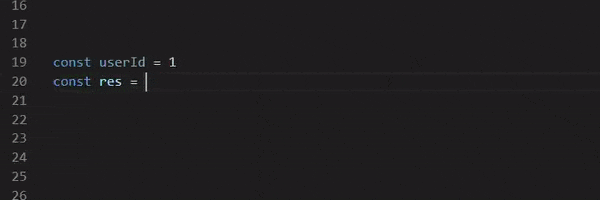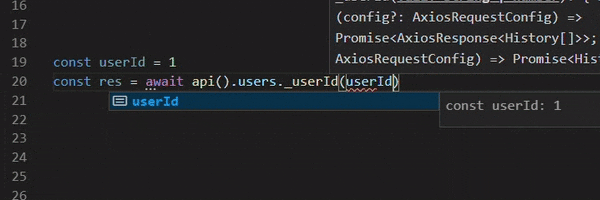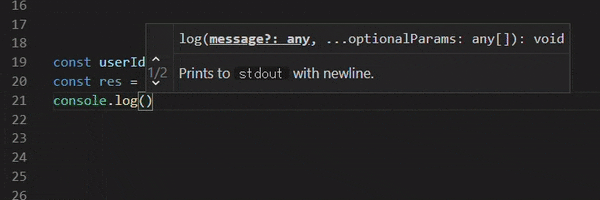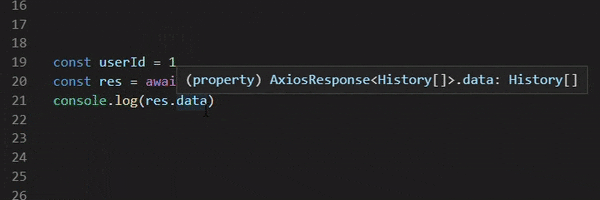TypeScript friendly HTTP client wrapper for the browser and node.js.
- Path, URL query, header, body, and response can all specify the type
- FormData / URLSearchParams content can also specify the type
- HTTP client supports axios / fetch / node-fetch
- Reproduce the endpoint directory structure in the "api" directory
- Export a Type alias named "Methods"
- Call "aspida" with npm scripts
- API type definition file "api/$api.ts" will be generated, so import the application and make an HTTP request
-
Using npm:
$ npm install aspida @aspida/axios axios
-
Using Yarn:
$ yarn add aspida @aspida/axios axios
$ mkdir apiDefineMethods<> is helper type for defining Methods. In earlier aspida, user shuold define without checking for API definition.
If you already have aspida in your projects, you can easily use DefineMethods<> with surrounding your definition.
It is just an option whether to use DefineMethods<>.
Be aware of the limitation that DefineMethods<> can't detect extra meaningless properties.
-
GET: /v1/users/?limit={number}
-
POST: /v1/users
api/v1/users/index.tsimport type { DefineMethods } from "aspida"; type User = { id: number; name: string; }; export type Methods = DefineMethods<{ get: { query?: { limit: number; }; resBody: User[]; }; post: { reqBody: { name: string; }; resBody: User; /** * reqHeaders(?): ... * reqFormat: ... * status: ... * resHeaders(?): ... * polymorph: [...] */ }; }>;
-
GET: /v1/users/${userId}
-
PUT: /v1/users/${userId}
api/v1/users/_userId@number/index.tsSpecify the type of path variable “userId” starting with underscore with “@number”
If not specified with @, the default path variable type is "number | string"import type { DefineMethods } from "aspida"; type User = { id: number; name: string; }; export type Methods = DefineMethods<{ get: { resBody: User; }; put: { reqBody: { name: string; }; resBody: User; }; }>;
package.json
{
"scripts": {
"api:build": "aspida"
}
}$ npm run api:build
> api/$api.ts was built successfully.src/index.ts
import aspida from "@aspida/axios";
import api from "../api/$api";
(async () => {
const userId = 0;
const limit = 10;
const client = api(aspida());
await client.v1.users.post({ body: { name: "taro" } });
const res = await client.v1.users.get({ query: { limit } });
console.log(res);
// req -> GET: /v1/users/?limit=10
// res -> { status: 200, body: [{ id: 0, name: "taro" }], headers: {...} }
const user = await client.v1.users._userId(userId).$get();
console.log(user);
// req -> GET: /v1/users/0
// res -> { id: 0, name: "taro" }
})();| Option | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
--config-c |
string |
"aspida.config.js" |
Specify the path to the configuration file. |
--watch-w |
Enable watch mode. Regenerate $api.ts according to
the increase / decrease of the API endpoint file.
|
||
--version-v |
Print aspida version. |
| Option | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| input | string | "api" | Specifies the endpoint type definition root directory |
| baseURL | string | "" | Specify baseURL of the request |
| trailingSlash | boolean | false | Append / to the request URL |
| outputEachDir | boolean | false | Generate $api.ts in each endpoint directory |
| outputMode (>=1.6.0) | "all" | "normalOnly" | "aliasOnly" | "all" | Output either get or $get for compression |
import { version, build, watch } from "aspida/dist/commands";
console.log(version()); // 0.x.y
build();
build("./app/aspida.config.js");
build({ input: "api1" });
build([
{ baseURL: "https://example.com/v1" },
{
input: "api2",
baseURL: "https://example.com/v2",
trailingSlash: true,
outputEachDir: true,
outputMode: "all",
},
]);
watch();
watch("./app/aspida.config.js");
watch({ input: "api1" });
watch([
{ baseURL: "https://example.com/v1" },
{
input: "api2",
baseURL: "https://example.com/v2",
trailingSlash: true,
outputEachDir: true,
outputMode: "all",
},
]);- openapi2aspida - Convert OpenAPI 3.0 and Swagger 2.0 definitions
- aspida-mock - TypeScript friendly RESTful API mock
- frourio - Fast and type-safe full stack framework, for TypeScript TypeScript
- @aspida/react-query - React Query wrapper
- @aspida/swr - SWR (React Hooks) wrapper
- @aspida/swrv - SWRV (Vue Composition API) wrapper
- eslint-plugin-aspida - Support writing aspida api definition
- Change the directory where type definition file is placed to other than "api"
- Serialize GET parameters manually
- POST with FormData
- POST with URLSearchParams
- Receive response with ArrayBuffer
- Define polymorphic request
- Define endpoints that contain special characters
- Import only some endpoints
- Retrieve endpoint URL string
- Reflect TSDoc comments
Create a configuration file at the root of the project
aspida.config.js
module.exports = { input: "src" };Specify baseURL in configuration file
module.exports = { baseURL: "https://example.com/api" };If you want to define multiple API endpoints, specify them in an array
module.exports = [{ input: "api1" }, { input: "api2", baseURL: "https://example.com/api" }];aspida leaves GET parameter serialization to standard HTTP client behavior
If you want to serialize manually, you can use config object of HTTP client
src/index.ts
import axios from "axios";
import qs from "qs";
import aspida from "@aspida/axios";
import api from "../api/$api";
(async () => {
const client = api(
aspida(axios, { paramsSerializer: params => qs.stringify(params, { indices: false }) })
);
const users = await client.v1.users.$get({
// config: { paramsSerializer: (params) => qs.stringify(params, { indices: false }) },
query: { ids: [1, 2, 3] },
});
console.log(users);
// req -> GET: /v1/users/?ids=1&ids=2&ids=3
// res -> [{ id: 1, name: "taro1" }, { id: 2, name: "taro2" }, { id: 3, name: "taro3" }]
})();api/v1/users/index.ts
import type { DefineMethods } from "aspida";
import type { ReadStream } from "fs";
export type Methods = DefineMethods<{
post: {
reqFormat: FormData;
reqBody: {
name: string;
icon: File | ReadStream;
};
resBody: {
id: number;
name: string;
};
};
}>;src/index.ts
import aspida from "@aspida/axios";
import api from "../api/$api";
(async () => {
const client = api(aspida());
const user = await client.v1.users.$post({
body: {
name: "taro",
icon: imageFile,
},
});
console.log(user);
// req -> POST: h/v1/users
// res -> { id: 0, name: "taro" }
})();Post in Node.js (>=1.6.0)
src/index.ts
import fs from "fs";
import aspida from "@aspida/axios";
import api from "../api/$api";
(async () => {
const client = api(aspida());
const fileName = "images/sample.jpg";
const user = await client.v1.users.$post({
body: {
name: "taro",
icon: fs.createReadStream(fileName),
},
});
console.log(user);
// req -> POST: h/v1/users
// res -> { id: 0, name: "taro" }
})();api/v1/users/index.ts
import type { DefineMethods } from "aspida";
export type Methods = DefineMethods<{
post: {
reqFormat: URLSearchParams;
reqBody: {
name: string;
};
resBody: {
id: number;
name: string;
};
};
}>;src/index.ts
import aspida from "@aspida/axios";
import api from "../api/$api";
(async () => {
const client = api(aspida());
const user = await client.v1.users.$post({ body: { name: "taro" } });
console.log(user);
// req -> POST: /v1/users
// res -> { id: 0, name: "taro" }
})();api/v1/users/index.ts
import type { DefineMethods } from "aspida";
export type Methods = DefineMethods<{
get: {
query: {
name: string;
};
resBody: ArrayBuffer;
};
}>;src/index.ts
import aspida from "@aspida/axios";
import api from "../api/$api";
(async () => {
const client = api(aspida());
const user = await client.v1.users.$get({ query: { name: "taro" } });
console.log(user);
// req -> GET: /v1/users/?name=taro
// res -> ArrayBuffer
})();api/users/index.ts
import type { DefineMethods } from 'aspida'
type User = {
id: number
name: string
}
export Methods = DefineMethods<{
post: {
// common properties
reqFormat: FormData
/**
* query(?): ...
* reqHeaders(?): ...
* reqBody(?): ...
* status: ...
* resHeaders(?): ...
* resBody(?): ...
*/
polymorph: [
// polymorphic types
{
reqBody: Omit<User, 'id'>
resBody: User
/**
* query(?): ...
* reqHeaders(?): ...
* status: ...
* resHeaders(?): ...
*/
},
{
reqBody: Omit<User, 'id'>[]
resBody: User[]
}
]
}
}>src/index.ts
import aspida from "@aspida/axios";
import api from "../api/$api";
(async () => {
const client = api(aspida());
const user = await client.users.$post({ body: { name: "taro" } });
console.log(user); // { id: 0, name: "taro" }
const users = await client.users.$post({
body: [{ name: "hanako" }, { name: "mario" }],
});
console.log(users); // [{ id: 1, name: "hanako" }, { id: 2, name: "mario" }]
})();Special characters are encoded as percent-encoding in the file name
Example ":" -> "%3A"
api/foo%3Abar/index.ts
import type { DefineMethods } from "aspida";
export type Methods = DefineMethods<{
get: {
resBody: string;
};
}>;api/users/_userId@number%3Aread/index.ts
import type { DefineMethods } from "aspida";
export type Methods = DefineMethods<{
get: {
resBody: User;
};
}>;With clients, "%3A" -> ":"
src/index.ts
import aspida from "@aspida/axios";
import api from "../api/$api";
(async () => {
const client = api(aspida());
const message = await client.foo_bar.$get();
console.log(message);
// req -> GET: /foo:bar
const user = await client.users._userId_read(1).$get();
console.log(user);
// req -> GET: /users/1:read
})();If you don't need to use all of api/$api.ts , you can split them up and import only part of them
outputEachDir option generates $api.ts in each endpoint directory
$api.ts will not be generated under the directory containing the path variable
aspida.config.js
module.exports = { outputEachDir: true };Import only $api.ts of the endpoint you want to use and put it into Object
src/index.ts
import aspida from "@aspida/axios";
import api0 from "../api/v1/foo/$api";
import api1 from "../api/v2/bar/$api";
(async () => {
const aspidaClient = aspida();
const client = {
foo: api0(aspidaClient),
bar: api1(aspidaClient),
};
const message = await client.bar._id(1).$get();
// req -> GET: /v2/bar/1
})();src/index.ts
import aspida from "@aspida/axios";
import api from "../api/$api";
(async () => {
const client = api(aspida());
console.log(client.v1.users.$path());
// /v1/users
console.log(client.vi.users.$path({ query: { limit: 10 } }));
// /v1/users?limit=10
console.log(
client.vi.users.$path({
method: "post",
query: { id: 1 },
})
);
// /v1/users?id=1
})();api/index.ts
import type { DefineMethods } from "aspida";
/**
* root comment
*
* @remarks
* root remarks comment
*/
export type Methods = DefineMethods<{
/**
* post method comment
*
* @remarks
* post method remarks comment
*/
post: {
/** post query comment */
query: { limit: number };
/** post reqHeaders comment */
reqHeaders: { token: string };
reqFormat: FormData;
/** post reqBody comment */
reqBody: UserCreation;
/**
* post resBody comment1
* post resBody comment2
*/
resBody: User;
};
}>;$ npm run api:buildapi/$api.ts
/**
* root comment
*
* @remarks
* root remarks comment
*/
const api = <T>({ baseURL, fetch }: AspidaClient<T>) => {
return {
/**
* post method comment
*
* @remarks
* post method remarks comment
*
* @param option.query - post query comment
* @param option.headers - post reqHeaders comment
* @param option.body - post reqBody comment
* @returns post resBody comment1
* post resBody comment2
*/
$post: (option: {
body: Methods0["post"]["reqBody"];
query: Methods0["post"]["query"];
headers: Methods0["post"]["reqHeaders"];
config?: T;
}) =>
fetch<Methods0["post"]["resBody"]>(prefix, PATH0, POST, option)
.json()
.then(r => r.body),
};
};aspida is licensed under a MIT License.